Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why does the rate of a reaction increase with rise in temperature?
उत्तर
At higher temperatures, larger fraction of colliding particles can cross the energy barrier (i.e. the activation energy), which leads to faster rate.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The activation energy for the reaction \[\ce{2 HI_{(g)} -> H2_{(g)} + I2_{(g)}}\] is 209.5 kJ mol−1 at 581K. Calculate the fraction of molecules of reactants having energy equal to or greater than activation energy?
The rate constant for the decomposition of N2O5 at various temperatures is given below:
| T/°C | 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 |
| 105 × k/s−1 | 0.0787 | 1.70 | 25.7 | 178 | 2140 |
Draw a graph between ln k and `1/"T"` and calculate the values of A and Ea. Predict the rate constant at 30º and 50ºC.
The decomposition of A into product has value of k as 4.5 × 103 s−1 at 10°C and energy of activation 60 kJ mol−1. At what temperature would k be 1.5 × 104 s−1?
What is the effect of adding a catalyst on Activation energy (Ea)
Consider figure and mark the correct option.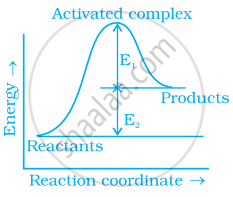
Which of the following statements are in accordance with the Arrhenius equation?
(i) Rate of a reaction increases with increase in temperature.
(ii) Rate of a reaction increases with decrease in activation energy.
(iii) Rate constant decreases exponentially with increase in temperature.
(iv) Rate of reaction decreases with decrease in activation energy.
Total number of vibrational degrees of freedom present in CO2 molecule is
The activation energy in a chemical reaction is defined as ______.
Explain how and why will the rate of reaction for a given reaction be affected when the temperature at which the reaction was taking place is decreased.
An exothermic reaction X → Y has an activation energy 30 kJ mol-1. If energy change ΔE during the reaction is - 20 kJ, then the activation energy for the reverse reaction in kJ is ______.
