Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Oxygen is available in plenty in air yet fuels do not burn by themselves at room temperature. Explain.
उत्तर
The activation energy for combustion reactions of fuels is very high at room temperature therefore they do not burn by themselves.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(b) Rate constant ‘k’ of a reaction varies with temperature ‘T’ according to the equation:
`logk=logA-E_a/2.303R(1/T)`
Where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for `logk Vs. 1/T` a straight line with a slope of −4250 K is obtained. Calculate ‘Ea’ for the reaction.(R = 8.314 JK−1 mol−1)
Consider the reaction
`3I_((aq))^-) +S_2O_8^(2-)->I_(3(aq))^-) + 2S_2O_4^(2-)`
At particular time t, `(d[SO_4^(2-)])/dt=2.2xx10^(-2)"M/s"`
What are the values of the following at the same time?
a. `-(d[I^-])/dt`
b. `-(d[S_2O_8^(2-)])/dt`
c. `-(d[I_3^-])/dt`
The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation k = `(4.5 xx 10^11 "s"^-1) "e"^(-28000 "K"//"T")`
Calculate Ea.
The decomposition of A into product has value of k as 4.5 × 103 s−1 at 10°C and energy of activation 60 kJ mol−1. At what temperature would k be 1.5 × 104 s−1?
Define activation energy.
Predict the main product of the following reactions: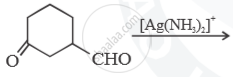
Total number of vibrational degrees of freedom present in CO2 molecule is
The activation energy in a chemical reaction is defined as ______.
Explain how and why will the rate of reaction for a given reaction be affected when the temperature at which the reaction was taking place is decreased.
What happens to the rate constant k and activation energy Ea as the temperature of a chemical reaction is increased? Justify.
