Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation k = `(4.5 xx 10^11 "s"^-1) "e"^(-28000 "K"//"T")`
Calculate Ea.
उत्तर
According to the Arrhenius equation, k = `"Ae"^((-"E"_"a")/("RT"))`
∴ `-"E"_"a"/("RT") = -(28000"K")/"T"`
E = 28000 K × R
= 28000 K × 8.314 JK−1 mol−1
= 232.79 kJ mol−1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain a graphical method to determine activation energy of a reaction.
Consider the reaction
`3I_((aq))^-) +S_2O_8^(2-)->I_(3(aq))^-) + 2S_2O_4^(2-)`
At particular time t, `(d[SO_4^(2-)])/dt=2.2xx10^(-2)"M/s"`
What are the values of the following at the same time?
a. `-(d[I^-])/dt`
b. `-(d[S_2O_8^(2-)])/dt`
c. `-(d[I_3^-])/dt`
The decomposition of A into product has value of k as 4.5 × 103 s−1 at 10°C and energy of activation 60 kJ mol−1. At what temperature would k be 1.5 × 104 s−1?
The rate constant of a first order reaction are 0.58 S-1 at 313 K and 0.045 S-1 at 293 K. What is the energy of activation for the reaction?
Define activation energy.
What is the effect of adding a catalyst on Activation energy (Ea)
Write a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order. Give an example of such a reaction. (Given : log2 = 0.3010,log 3 = 0.4771, log5 = 0.6990).
Predict the main product of the following reactions: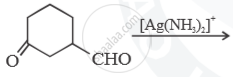
The rate of chemical reaction becomes double for every 10° rise in temperature because of ____________.
Why does the rate of a reaction increase with rise in temperature?
Thermodynamic feasibility of the reaction alone cannot decide the rate of the reaction. Explain with the help of one example.
Why in the redox titration of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] vs oxalic acid, we heat oxalic acid solution before starting the titration?
Match the statements given in Column I and Column II
| Column I | Column I | |
| (i) | Catalyst alters the rate of reaction | (a) cannot be fraction or zero |
| (ii) | Molecularity | (b) proper orientation is not there always |
| (iii) | Second half life of first order reaction | (c) by lowering the activation energy |
| (iv) | `e^((-E_a)/(RT)` | (d) is same as the first |
| (v) | Energetically favourable reactions (e) total probability is one are sometimes slow | (e) total probability is one |
| (vi) | Area under the Maxwell Boltzman curve is constant | (f) refers to the fraction of molecules with energy equal to or greater than activation energy |
In respect of the eqn k = \[\ce{Ae^{{-E_a}/{RT}}}\] in chemical kinetics, which one of the following statement is correct?
Arrhenius equation can be represented graphically as follows:

The (i) intercept and (ii) slope of the graph are:
Explain how and why will the rate of reaction for a given reaction be affected when the temperature at which the reaction was taking place is decreased.
A schematic plot of ln Keq versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
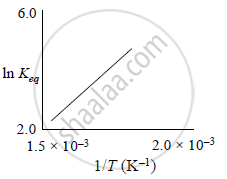
The reaction must be:
