Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The activation energy for the reaction \[\ce{2 HI_{(g)} -> H2_{(g)} + I2_{(g)}}\] is 209.5 kJ mol−1 at 581K. Calculate the fraction of molecules of reactants having energy equal to or greater than activation energy?
उत्तर
In the given case:
Ea = 209.5 kJ mol−1
T = 581 K
R = 8.314 JK−1 mol−1
Now, the fraction of molecules of reactants having energy equal to or greater than activation energy is given as:
x = `"n"/"N"`
x = `e^((-E_a)/"RT")`
In x = `- (E_a)/"RT"`
or, log x = `-E_a/(2.303 "RT")`
or, log x = `-(209.5 xx 10^3 "J mol"^-1)/(2.303 xx 8.314 "JK"^-1 "mol"^-1 xx 581 "K")`
= −18.8323
x = antilog (−18.8323)
= antilog 19.1677
= 1.471 × 10−19
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain a graphical method to determine activation energy of a reaction.
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 4 × 10−2 to 8 × 10−2 when the temperature changes from 27°C to 37°C. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea). (log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
What will be the effect of temperature on rate constant?
The rate of the chemical reaction doubles for an increase of 10 K in absolute temperature from 298 K. Calculate Ea.
The rate constant for the decomposition of hydrocarbons is 2.418 × 10−5 s−1 at 546 K. If the energy of activation is 179.9 kJ/mol, what will be the value of pre-exponential factor?
In the Arrhenius equation for a first order reaction, the values of ‘A’ of ‘Ea’ are 4 x 1013 sec-1 and 98.6 kJ mol-1 respectively. At what temperature will its half life period be 10 minutes?
[R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1]
Define activation energy.
Calculate activation energy for a reaction of which rate constant becomes four times when temperature changes from 30 °C to 50 °C. (Given R = 8.314 JK−1 mol−1).
Explain the following terms :
Half life period of a reaction (t1/2)
Write a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order. Give an example of such a reaction. (Given : log2 = 0.3010,log 3 = 0.4771, log5 = 0.6990).
Predict the main product of the following reactions: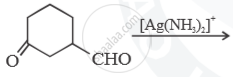
The chemical reaction in which reactants require high amount of activation energy are generally ____________.
During decomposition of an activated complex:
(i) energy is always released
(ii) energy is always absorbed
(iii) energy does not change
(iv) reactants may be formed
Which of the following statements are in accordance with the Arrhenius equation?
(i) Rate of a reaction increases with increase in temperature.
(ii) Rate of a reaction increases with decrease in activation energy.
(iii) Rate constant decreases exponentially with increase in temperature.
(iv) Rate of reaction decreases with decrease in activation energy.
The reaction between \[\ce{H2(g)}\] and \[\ce{O2(g)}\] is highly feasible yet allowing the gases to stand at room temperature in the same vessel does not lead to the formation of water. Explain.
Why in the redox titration of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] vs oxalic acid, we heat oxalic acid solution before starting the titration?
What happens to most probable kinetic energy and the energy of activation with increase in temperature?
The rate constant for a reaction is 1.5 × 10–7 sec–1 at 50°C. What is the value of activation energy?
The slope of Arrhenius Plot `("In" "k" "v"//"s" 1/"T")` of first-order reaction is −5 × 103 K. The value of Ea of the reaction is. Choose the correct option for your answer. [Given R = 8.314 JK−1mol−1]
A first-order reaction is 50% complete in 30 minutes at 300 K and in 10 minutes at 320 K. Calculate activation energy (Ea) for the reaction. [R = 8.314 J K−1 mol−1]
[Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021]
