Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The decomposition of a hydrocarbon has value of rate constant as 2.5×104s-1 At 27° what temperature would rate constant be 7.5×104 × 3 s-1if energy of activation is 19.147 × 103 J mol-1 ?
उत्तर
log `K_2/K_1= Ea /(2.303 R) [(T_2 - T_1)/(T_1T_2)]`
`T_1 -> 300k-> 2.5 xx 10^4 s^-2 → K_2`
`T_1 -> 300k-> 2.5 xx 10^4 s^-2 → K_2`
log `(7.5xx10^4(T-300))/(19.15 (300T))`
⇒ `0.477/1000 xx 300T = (T-300)1000`
⇒ 143T = 1000T - 300000
⇒ 300000 = 1000T - 143T
= 857 T
`T = 300000/857 = 350 K`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(b) Rate constant ‘k’ of a reaction varies with temperature ‘T’ according to the equation:
`logk=logA-E_a/2.303R(1/T)`
Where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for `logk Vs. 1/T` a straight line with a slope of −4250 K is obtained. Calculate ‘Ea’ for the reaction.(R = 8.314 JK−1 mol−1)
The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation k = `(4.5 xx 10^11 "s"^-1) "e"^(-28000 "K"//"T")`
Calculate Ea.
Predict the main product of the following reactions: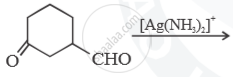
During decomposition of an activated complex:
(i) energy is always released
(ii) energy is always absorbed
(iii) energy does not change
(iv) reactants may be formed
Which of the following statements are in accordance with the Arrhenius equation?
(i) Rate of a reaction increases with increase in temperature.
(ii) Rate of a reaction increases with decrease in activation energy.
(iii) Rate constant decreases exponentially with increase in temperature.
(iv) Rate of reaction decreases with decrease in activation energy.
The reaction between \[\ce{H2(g)}\] and \[\ce{O2(g)}\] is highly feasible yet allowing the gases to stand at room temperature in the same vessel does not lead to the formation of water. Explain.
For an endothermic reaction energy of activation is Ea and enthalpy of reaction ΔH (both of there in KJ moI–1) minimum value of Ea will be
The rate constant for a reaction is 1.5 × 10–7 sec–1 at 50°C. What is the value of activation energy?
The activation energy of one of the reactions in a biochemical process is 532611 J mol–1. When the temperature falls from 310 K to 300 K, the change in rate constant observed is k300 = x × 10–3 k310. The value of x is ______.
[Given: ln 10 = 2.3, R = 8.3 J K–1 mol–1]
It is generally observed that the rate of a chemical reaction becomes double with every 10oC rise in temperature. If the generalisation holds true for a reaction in the temperature range of 298K to 308K, what would be the value of activation energy (Ea) for the reaction?
