Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 2 × 10−2 to 4 × 10−2 when the temperature changes from 300 K to 310 K. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea).
(log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
उत्तर
According to the Arrhenius equation,
k=Ae(−Ea/RT)
From this, we get
`"log"k_2/k_1=E_a/(2.303R)((T_2-T_1)/(T_1T_2))`
We are given that
Initial temperature, T1=300 K
Final temperature, T2=310 K
Rate constant at initial temperature, k1=2×10−2
Rate constant at final temperature, k2=4×10−2
Gas constant, R=8.314 J K−1 mol−1
Substituting the values, we get
`"log"((4xx10^(-2))/(2xx10^(-2)))=E_a/(2.303xx8.314)((310-300)/(300xx310))`
`therefore " activation energy of the reaction, "E_a=(log2xx2.303xx8.314xx300xx310)/10`
`=535985.94" J mol"^(-1)`
`=535.98" kJ mol"^(-1)`
संबंधित प्रश्न
Consider the reaction
`3I_((aq))^-) +S_2O_8^(2-)->I_(3(aq))^-) + 2S_2O_4^(2-)`
At particular time t, `(d[SO_4^(2-)])/dt=2.2xx10^(-2)"M/s"`
What are the values of the following at the same time?
a. `-(d[I^-])/dt`
b. `-(d[S_2O_8^(2-)])/dt`
c. `-(d[I_3^-])/dt`
The activation energy for the reaction \[\ce{2 HI_{(g)} -> H2_{(g)} + I2_{(g)}}\] is 209.5 kJ mol−1 at 581K. Calculate the fraction of molecules of reactants having energy equal to or greater than activation energy?
The rate constant for the decomposition of N2O5 at various temperatures is given below:
| T/°C | 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 |
| 105 × k/s−1 | 0.0787 | 1.70 | 25.7 | 178 | 2140 |
Draw a graph between ln k and `1/"T"` and calculate the values of A and Ea. Predict the rate constant at 30º and 50ºC.
Consider a certain reaction \[\ce{A -> Products}\] with k = 2.0 × 10−2 s−1. Calculate the concentration of A remaining after 100 s if the initial concentration of A is 1.0 mol L−1.
What is the effect of adding a catalyst on Activation energy (Ea)
Predict the main product of the following reactions: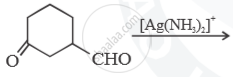
The rate of chemical reaction becomes double for every 10° rise in temperature because of ____________.
Why does the rate of a reaction increase with rise in temperature?
In respect of the eqn k = \[\ce{Ae^{{-E_a}/{RT}}}\] in chemical kinetics, which one of the following statement is correct?
What happens to the rate constant k and activation energy Ea as the temperature of a chemical reaction is increased? Justify.
