Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Rate law for the reaction \[\ce{A + 2B -> C}\] is found to be Rate = k [A][B]. Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be ______.
पर्याय
the same
doubled
quadrupled
halved
उत्तर
Rate law for the reaction \[\ce{A + 2B -> C}\] is found to be Rate = k [A][B]. Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be doubled.
Explanation:
The rate concentration of a reaction does not depend upon concentrations of the reactions. Hence, it will remain the same. Even if the equation shows the double concentration level even the rate concentration doubles so it's the same throughout.
Following with the equation \[\ce{A + 2B -> C}\]
If rate considered as (1) Rate1 = k[A][B]
If rate considered as 2
Then, Rate1 = k[A][2B]
Rate2 = 2Rate1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
(i) Write the differential rate equation.
(ii) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of A three times?
(iii) How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
Write molecularity of the following reaction:
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g)
For a reaction : 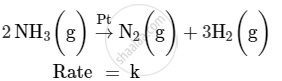
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
Write the principle behind the following methods of refining:
Hydraulic washing
Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
\[\ce{A(g) + 2B(g) -> 2C(g)}\]
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.
| Experiment | Initial concentration of [A]/mol L–¹ |
Initial concentration of [B]/mol L–¹ |
Initial rate of formation of [C]/mol L–¹ s–¹ |
| 1. | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2. | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
| 3. | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?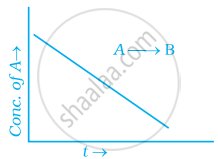
A catalyst in a reaction changes which of the following?
For a reaction \[\ce{Cl2l(g) + 2No(g) -> 2NaCl(g)}\] the rate law is expressed as rate= K[Cl2] [No]2 what is the order of the reaction?
If the 0.05 molar solution of m+ is replaced by a 0.0025 molar m+ solution, then the magnitude of the cell potential would be
Which of the following statement is true?
