Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write molecularity of the following reaction:
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g)
उत्तर १
2NO+O2→2NO2
Molecularity of reaction = 3
उत्तर २
The molecularity of the reaction is 3.
Explanation :
Molecularity : It is defined as the total number of reactant molecules taking part in the balanced equation of a reaction. It is a theoretical concept.
The given balanced chemical reaction is,
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g)
In this reaction, 2 NO molecules reacts with the 1 Oxygen molecule.Total number of reactant molecule = 2 + 1 = 3
Therefore, the molecularity of the reaction is 3.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define “zero order reaction”.
For a reaction : 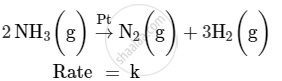
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
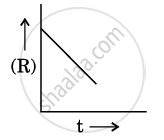
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume :
SO2Cl2 (g) → SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
| Experiment | Time/s–1 | Total pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.7 |
Calculate the rate constant.
(Given : log 4 = 0.6021, log 2 = 0.3010)
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
For the reaction: \[\ce{2A + B → A2B}\] the rate = k[A][B]2 with k = 2.0 × 10−6 mol−2 L2 s−1. Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0.1 mol L−1, [B] = 0.2 mol L−1. Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L−1.
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. Write the differential rate equation.
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of B three times?
Write the principle behind the following methods of refining:
Hydraulic washing
Define the following terms:
Half-life period of reaction (t1/2).
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
Rate law for the reaction \[\ce{A + 2B -> C}\] is found to be Rate = k [A][B]. Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be ______.
Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
\[\ce{A(g) + 2B(g) -> 2C(g)}\]
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.
| Experiment | Initial concentration of [A]/mol L–¹ |
Initial concentration of [B]/mol L–¹ |
Initial rate of formation of [C]/mol L–¹ s–¹ |
| 1. | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2. | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
| 3. | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
Consider the reaction A ⇌ B. The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
For a complex reaction:
(i) order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
(ii) order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
(iii) order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
(iv) molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non interger.
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?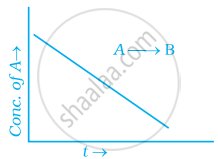
Why is the probability of reaction with molecularity higher than three very rare?
Why can’t molecularity of any reaction be equal to zero?
Why molecularity is applicable only for elementary reactions and order is applicable for elementary as well as complex reactions?
Why can we not determine the order of a reaction by taking into consideration the balanced chemical equation?
In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction.
For a first order A → B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 m is found to be 2.0 × 10–5. The half-life period of reaction.
If the 0.05 molar solution of m+ is replaced by a 0.0025 molar m+ solution, then the magnitude of the cell potential would be
The half-life period of a. substance in a certain enzyme catalysed reaction is 138 s. The time required for the concentration of the substance to fall from 1.28 mol–1 to 0.04 mg L–1 is
The following data was obtained for chemical reaction given below at 975 K.
\[\ce{2NO(g) + 2H2(g) -> N2(g) + 2H2O(g)}\]
| [NO] | [H2] | Rate | |
| Mol L-1 | Mol L-1 | Mol L-1 s-1 | |
| (1) | 8 × 10-5 | 8 × 10-5 | 7 × 10-9 |
| (2) | 24 × 10-5 | 8 × 10-5 | 2.1 × 10-8 |
| (3) | 24 × 10-5 | 32 × 10-5 | 8.4 × 10-8 |
The order of the reaction with respect to NO is ______. (Integer answer)
Which of the following statement is true?
