Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define “zero order reaction”.
उत्तर
Zero order reaction is the reaction whose rate is independent of the reactant concentration and remains constant throughout the course of the reaction.
संबंधित प्रश्न
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
For a reaction : 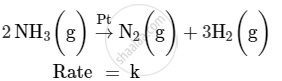
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
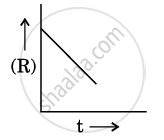
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
For a reaction, \[\ce{A + B -> Product}\]; the rate law is given by, `r = k[A]^(1/2)[B]^2`. What is the order of the reaction?
The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y?
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{C2H5Cl_{(g)} -> C2H4_{(g)} + HCl_{(g)}}\] Rate = k [C2H5Cl]
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. Write the differential rate equation.
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of B three times?
In a reaction between A and B, the initial rate of reaction (r0) was measured for different initial concentrations of A and B as given below:
| A/mol L−1 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.40 |
| B/mol L−1 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| r0/mol L−1 s−1 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 1.43 × 10−4 |
What is the order of the reaction with respect to A and B?
Write resonating structures of ozone.
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
Which of the following statement is true for order of a reaction?
Consider a first order gas phase decomposition reaction given below :
\[\ce{A(g) -> B(g) + C(g)}\]
The initial pressure of the system before decomposition of A was pi. After lapse of time ‘t’, total pressure of the system increased by x units and became ‘pt’ The rate constant k for the reaction is given as ______.
For a complex reaction:
(i) order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
(ii) order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
(iii) order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
(iv) molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non interger.
In a reaction if the concentration of reactant A is tripled, the rate of reaction becomes twenty seven times. What is the order of the reaction?
Why can’t molecularity of any reaction be equal to zero?
Assertion: Order of the reaction can be zero or fractional.
Reason: We cannot determine order from balanced chemical equation.
Use Molecular Orbital theory to determine the bond order in each of species, [He2j+ and [He2]2+?
The role of a catalyst is to change
The rate of a chemical reaction double for every 10° rise in temperature. If the temperature is raised. by 50°C, the rate of relation by about:-
For a reaction 1/2 A ⇒ 2B, rate of disappearance of A is related 't o the appearance of B by the expression:
For reaction 2A + B → BC + D which of the following does not Express the reaction rates
Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow:
|
The rate of reaction is concerned with decrease in the concentration of reactants or increase in the concentration of products per unit of time. It can be expressed as instantaneous rate at a particular instant of time and average rate over a large interval of time. A number of factors such as temperature, concentration of reactants, catalyst affect the rate of reaction. Mathematical representation of rate of a reaction is given by rate law: Rate = k[A]x [B]y x and y indicate how sensitive the rate is to change in concentration of A and B. Sum of x + y gives the overall order of a reaction. |
- What is the effect of temperature on the rate constant of a reason? [1]
- For a reaction \[\ce{A + B → Product}\], the rate law is given by, Rate = k[A]2 [B]1/2. What is the order of the reaction? [1]
- How order and molecularity are different for complex reactions? [1]
- A first-order reaction has a rate constant 2 × 10–3 s–1. How long will 6 g of this reactant take to reduce to 2 g? [2]
OR
The half-life for radioactive decay of 14C is 6930 years. An archaeological artifact containing wood had only 75% of the 14C found in a living tree. Find the age of the sample.
[log 4 = 0.6021, log 3 = 0.4771, log 2 = 0.3010, log 10 = 1] [2]
For a chemical reaction starting with some initial concentration of reactant At as a function of time (t) is given by the equation,
`1/("A"_"t"^4) = 2 + 1.5 xx 10^-3` t
The rate of disappearance of [A] is ____ × 10-2 M/sec when [A] = 2 M.
[Given: [At] in M and t in sec.]
[Express your answer in terms of 10-2 M /s]
[Round off your answer if required]
Assertion (A): Order of reaction is applicable to elementary as well as complex reactions.
Reason (R): For a complex reaction, molecularity has no meaning.
Which of the following statement is true?
