Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. Write the differential rate equation.
उत्तर
The differential rate equation will be
`(dx)/dt = k[A][B]^2`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A → B is a first order reaction with rate 6.6 × 10-5m-s-1. When [A] is 0.6m, rate constant of the reaction is
- 1.1 × 10-5s-1
- 1.1 × 10-4s-1
- 9 × 10-5s-1
- 9 × 10-4s-1
For a reaction: 
Rate = k
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
Write two factors that affect the rate of reaction.
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of B is doubled?
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
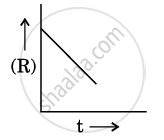
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
Write the principle behind the following methods of refining:
Hydraulic washing
Define the following terms:
Pseudo first-order reaction
Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
\[\ce{A(g) + 2B(g) -> 2C(g)}\]
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.
| Experiment | Initial concentration of [A]/mol L–¹ |
Initial concentration of [B]/mol L–¹ |
Initial rate of formation of [C]/mol L–¹ s–¹ |
| 1. | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2. | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
| 3. | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
The value of rate constant of a pseudo first order reaction ______.
Consider the reaction A ⇌ B. The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
The role of a catalyst is to change
In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction.
For a reaction A + B → products, the rate law is given by: r = `K[A]^(1/2)`. What is the order of reaction?
The rate constant for the reaction \[\ce{2H2O5 -> 4NO2 + O2}\] is 30 × 10–5 sec–1. if the rate is 204 × 10–5 mol L–1 S–1, then the concentration of N2O5 (in mol–1) is-
If the 0.05 molar solution of m+ is replaced by a 0.0025 molar m+ solution, then the magnitude of the cell potential would be
On heating compound (A) gives a gas (B) which is constituent of air. The gas when treated with H2 in the presence of catalyst gives another gas (C) which is basic in nature, (A) should not be ______.
