Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
उत्तर
When the concentrations of both A and B are doubled,
Rate = k(2a) (2b)2
= 8kab2
Therefore, the rate of reaction will increase 8 times.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define “zero order reaction”.
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
For a reaction : 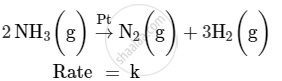
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
Write resonating structures of ozone.
Define the following terms:
Half-life period of reaction (t1/2).
Which of the following statements is not correct about order of a reaction.
For a complex reaction:
(i) order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
(ii) order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
(iii) order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
(iv) molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non interger.
In a reaction if the concentration of reactant A is tripled, the rate of reaction becomes twenty seven times. What is the order of the reaction?
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?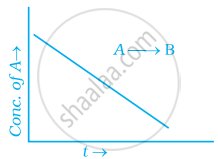
Assertion: The enthalpy of reaction remains constant in the presence of a catalyst.
Reason: A catalyst participating in the reaction, forms different activated complex and lowers down the activation energy but the difference in energy of reactant and product remains the same.
For a reaction \[\ce{Cl2l(g) + 2No(g) -> 2NaCl(g)}\] the rate law is expressed as rate= K[Cl2] [No]2 what is the order of the reaction?
The rate of a chemical reaction double for every 10° rise in temperature. If the temperature is raised. by 50°C, the rate of relation by about:-
For a reaction 1/2 A ⇒ 2B, rate of disappearance of A is related 't o the appearance of B by the expression:
The conversion of molecules A to B follow second order kinetics. If concentration of A is increased to three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B?
On heating compound (A) gives a gas (B) which is constituent of air. The gas when treated with H2 in the presence of catalyst gives another gas (C) which is basic in nature, (A) should not be ______.
For a chemical reaction starting with some initial concentration of reactant At as a function of time (t) is given by the equation,
`1/("A"_"t"^4) = 2 + 1.5 xx 10^-3` t
The rate of disappearance of [A] is ____ × 10-2 M/sec when [A] = 2 M.
[Given: [At] in M and t in sec.]
[Express your answer in terms of 10-2 M /s]
[Round off your answer if required]
Which of the following statement is true?
