Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the following terms:
Half-life period of reaction (t1/2).
उत्तर
For zero-order reaction,
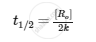
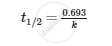
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A → B is a first order reaction with rate 6.6 × 10-5m-s-1. When [A] is 0.6m, rate constant of the reaction is
- 1.1 × 10-5s-1
- 1.1 × 10-4s-1
- 9 × 10-5s-1
- 9 × 10-4s-1
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
For the reaction: \[\ce{2A + B → A2B}\] the rate = k[A][B]2 with k = 2.0 × 10−6 mol−2 L2 s−1. Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0.1 mol L−1, [B] = 0.2 mol L−1. Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L−1.
Which of the following statement is true for order of a reaction?
Which of the following statements is not correct about order of a reaction.
In any unimolecular reaction:
(i) only one reacting species is involved in the rate determining step.
(ii) the order and the molecularity of slowest step are equal to one.
(iii) the molecularity of the reaction is one and order is zero.
(iv) both molecularity and order of the reaction are one.
For a complex reaction:
(i) order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
(ii) order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
(iii) order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
(iv) molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non interger.
In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction.
For a chemical reaction starting with some initial concentration of reactant At as a function of time (t) is given by the equation,
`1/("A"_"t"^4) = 2 + 1.5 xx 10^-3` t
The rate of disappearance of [A] is ____ × 10-2 M/sec when [A] = 2 M.
[Given: [At] in M and t in sec.]
[Express your answer in terms of 10-2 M /s]
[Round off your answer if required]
Assertion (A): Order of reaction is applicable to elementary as well as complex reactions.
Reason (R): For a complex reaction, molecularity has no meaning.
