Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of B three times?
उत्तर
If the concentration of B is increased three times, then
`-(d[R])/dt` = k[A][3B]2
= 9k[A][B]2
∴ the rate of reaction will increase 9 times.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A → B is a first order reaction with rate 6.6 × 10-5m-s-1. When [A] is 0.6m, rate constant of the reaction is
- 1.1 × 10-5s-1
- 1.1 × 10-4s-1
- 9 × 10-5s-1
- 9 × 10-4s-1
What is pseudo first order reaction? Give one· example of it.
Write molecularity of the following reaction:
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g)
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{CH3CHO_{(g)} -> CH4_{(g)} + CO_{(g)}}\] Rate = k [CH3CHO]3/2
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. Write the differential rate equation.
The decomposition of N2O5(g) at 320K according to the following equation follows first order reaction:
`N_2O_(5(g))->2NO_(2(g))+1/2O_(2(g))`
The initial concentration of N2O5(g) is 1.24 x 10-2 mol. L-1 and after 60 minutes 0.20x10-2 molL-1. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction at 320K.
Which of the following statement is true for order of a reaction?
Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
\[\ce{A(g) + 2B(g) -> 2C(g)}\]
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.
| Experiment | Initial concentration of [A]/mol L–¹ |
Initial concentration of [B]/mol L–¹ |
Initial rate of formation of [C]/mol L–¹ s–¹ |
| 1. | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2. | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
| 3. | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?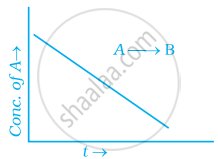
Why does the rate of any reaction generally decreases during the course of the reaction?
Match the graph given in Column I with the order of reaction given in Column II. More than one item in Column I may link to the same item of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) |  |
|
| (ii) |  |
(a) 1st order |
| (iii) |  |
(b) Zero-order |
| (iv) |  |
Use Molecular Orbital theory to determine the bond order in each of species, [He2j+ and [He2]2+?
For a reaction \[\ce{Cl2l(g) + 2No(g) -> 2NaCl(g)}\] the rate law is expressed as rate= K[Cl2] [No]2 what is the order of the reaction?
The rate of a chemical reaction double for every 10° rise in temperature. If the temperature is raised. by 50°C, the rate of relation by about:-
The number of molecules of the reactants taking part in a single step of the reaction is indicative of ______.
For a chemical reaction starting with some initial concentration of reactant At as a function of time (t) is given by the equation,
`1/("A"_"t"^4) = 2 + 1.5 xx 10^-3` t
The rate of disappearance of [A] is ____ × 10-2 M/sec when [A] = 2 M.
[Given: [At] in M and t in sec.]
[Express your answer in terms of 10-2 M /s]
[Round off your answer if required]
