Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of B three times?
उत्तर
If the concentration of B is increased three times, then
`-(d[R])/dt` = k[A][3B]2
= 9k[A][B]2
∴ the rate of reaction will increase 9 times.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a first order reaction x → y, 40% of the given sample of compound remains unreacted in 45 minutes. Calculate rate constant of the reaction.
A → B is a first order reaction with rate 6.6 × 10-5m-s-1. When [A] is 0.6m, rate constant of the reaction is
- 1.1 × 10-5s-1
- 1.1 × 10-4s-1
- 9 × 10-5s-1
- 9 × 10-4s-1
Write molecularity of the following reaction:
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g)
For the first order thermal decomposition reaction, the following data were obtained:
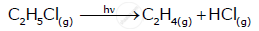
Time / sec Totalpressure / atm
0 0.30
300 0.50
Calculate the rate constant
(Given: log 2 = 0.301, log3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
For a reaction : 
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{C2H5Cl_{(g)} -> C2H4_{(g)} + HCl_{(g)}}\] Rate = k [C2H5Cl]
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. Write the differential rate equation.
How does calcination differ from roasting?
Define the following terms:
Pseudo first-order reaction
Match the graph given in Column I with the order of reaction given in Column II. More than one item in Column I may link to the same item of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) |  |
|
| (ii) |  |
(a) 1st order |
| (iii) |  |
(b) Zero-order |
| (iv) |  |
Assertion: Order of the reaction can be zero or fractional.
Reason: We cannot determine order from balanced chemical equation.
For a first order A → B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 m is found to be 2.0 × 10–5. The half-life period of reaction.
The rate of a chemical reaction double for every 10° rise in temperature. If the temperature is raised. by 50°C, the rate of relation by about:-
At concentration of 0.1 and 0.2 mol L–1 the rates of deem position of a compound were found to be 0.18 and 0.72 mol L–1 m–1. What is the order of the reaction?
The number of molecules of the reactants taking part in a single step of the reaction is indicative of ______.
For a chemical reaction starting with some initial concentration of reactant At as a function of time (t) is given by the equation,
`1/("A"_"t"^4) = 2 + 1.5 xx 10^-3` t
The rate of disappearance of [A] is ____ × 10-2 M/sec when [A] = 2 M.
[Given: [At] in M and t in sec.]
[Express your answer in terms of 10-2 M /s]
[Round off your answer if required]
A flask contains a mixture of compounds A and B. Both compounds decompose by first-order kinetics. The half-lives for A and B are 300 s and 180 s, respectively. If the concentrations of A and B are equal initially, the time required for the concentration of A to be four times that of B (in s) is ______. (Use ln 2 = 0.693)
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is reduced to half?
