Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How does calcination differ from roasting?
उत्तर
| Roasting | Calcination |
| Ore is heated in excess of air. | Ore is heated in the absence or limited supply of air. |
| This is used for sulphide ores. | This is used for carbonate ores. |
| SO2 is produced along with metal oxide. | CO2 is produced along with metal oxide. |
| e.g. \[\ce{ 2ZnS + 3O2 ->[\Delta] 2ZnO + 2SO2}\] | e.g. \[\ce{ZnCO3 ->[\Delta] ZnO + CO2}\] |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a first order reaction x → y, 40% of the given sample of compound remains unreacted in 45 minutes. Calculate rate constant of the reaction.
For a reaction: 
Rate = k
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
For a reaction : 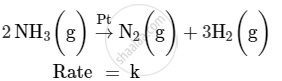
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
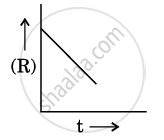
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{H2O2_{( aq)} + 3I^-_{( aq)} + 2H^+ -> 2H2O_{(l)} + I^-_3}\] Rate = k[H2O2][I−]
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is doubled?
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
Define the following terms:
Half-life period of reaction (t1/2).
Rate of reaction for the combustion of propane is equal to:
\[\ce{C3H8_{(g)} + 5O2_{(g)} -> 3CO2_{(g)} + 4H2O_{(g)}}\]
What is the order of a reaction which has a rate expression; Rate = `"k"["A"]^(3/2)["B"]^1`?
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
Rate law for the reaction \[\ce{A + 2B -> C}\] is found to be Rate = k [A][B]. Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be ______.
Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
\[\ce{A(g) + 2B(g) -> 2C(g)}\]
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.
| Experiment | Initial concentration of [A]/mol L–¹ |
Initial concentration of [B]/mol L–¹ |
Initial rate of formation of [C]/mol L–¹ s–¹ |
| 1. | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2. | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
| 3. | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
The value of rate constant of a pseudo first order reaction ______.
Consider the reaction A ⇌ B. The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
For a complex reaction:
(i) order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
(ii) order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
(iii) order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
(iv) molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non interger.
Why molecularity is applicable only for elementary reactions and order is applicable for elementary as well as complex reactions?
Match the graph given in Column I with the order of reaction given in Column II. More than one item in Column I may link to the same item of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) |  |
|
| (ii) |  |
(a) 1st order |
| (iii) |  |
(b) Zero-order |
| (iv) |  |
Assertion: Order and molecularity are same.
Reason: Order is determined experimentally and molecularity is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficient of rate determining elementary step.
Assertion: The enthalpy of reaction remains constant in the presence of a catalyst.
Reason: A catalyst participating in the reaction, forms different activated complex and lowers down the activation energy but the difference in energy of reactant and product remains the same.
Assertion: Rate constants determined from Arrhenius equation are fairly accurate for simple as well as complex molecules.
Reason: Reactant molecules undergo chemical change irrespective of their orientation during collision.
Use Molecular Orbital theory to determine the bond order in each of species, [He2j+ and [He2]2+?
In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction.
For a first order A → B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 m is found to be 2.0 × 10–5. The half-life period of reaction.
The number of molecules of the reactants taking part in a single step of the reaction is indicative of ______.
Identify the order of reaction from the following unit for its rate constant:
L mol–1s–1
