Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Assertion: Order and molecularity are same.
Reason: Order is determined experimentally and molecularity is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficient of rate determining elementary step.
विकल्प
Both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Both assertion and reason are correct but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
उत्तर
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
Explanation:
Order and molecularity may not be necessarily same. Order is determined experimentally but molecularity is calculated using balanced stoichiometric equation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A → B is a first order reaction with rate 6.6 × 10-5m-s-1. When [A] is 0.6m, rate constant of the reaction is
- 1.1 × 10-5s-1
- 1.1 × 10-4s-1
- 9 × 10-5s-1
- 9 × 10-4s-1
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
For a reaction : 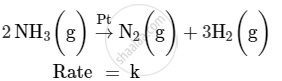
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
What is the order of a reaction which has a rate expression; Rate = `"k"["A"]^(3/2)["B"]^1`?
Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
\[\ce{A(g) + 2B(g) -> 2C(g)}\]
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.
| Experiment | Initial concentration of [A]/mol L–¹ |
Initial concentration of [B]/mol L–¹ |
Initial rate of formation of [C]/mol L–¹ s–¹ |
| 1. | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2. | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
| 3. | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?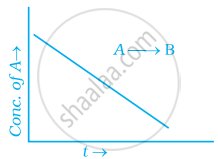
Why can we not determine the order of a reaction by taking into consideration the balanced chemical equation?
For reaction 2A + B → BC + D which of the following does not Express the reaction rates
For the reaction, \[\ce{A +2B → AB2}\], the order w.r.t. reactant A is 2 and w.r.t. reactant B. What will be change in rate of reaction if the concentration of A is doubled and B is halved?
Which of the following statement is true?
