Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For a reaction : 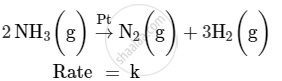
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
उत्तर
(i) This reaction is catalysed by Pt at high pressure. So, it is a zero-order reaction with molecularity 2.
(ii) The rate law expression for this reaction is
Rate = k
Hence, the unit of k is mol L−1 s−1.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
(i) Write the differential rate equation.
(ii) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of A three times?
(iii) How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{CH3CHO_{(g)} -> CH4_{(g)} + CO_{(g)}}\] Rate = k [CH3CHO]3/2
Assertion: Order and molecularity are same.
Reason: Order is determined experimentally and molecularity is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficient of rate determining elementary step.
Assertion: Rate constants determined from Arrhenius equation are fairly accurate for simple as well as complex molecules.
Reason: Reactant molecules undergo chemical change irrespective of their orientation during collision.
A catalyst in a reaction changes which of the following?
The role of a catalyst is to change
For a reaction R → p the concentration of reactant change from 0.03 m to 0.02 m in minute, calculate the average rate of the reaction using the unit of second.
If the 0.05 molar solution of m+ is replaced by a 0.0025 molar m+ solution, then the magnitude of the cell potential would be
For a chemical reaction starting with some initial concentration of reactant At as a function of time (t) is given by the equation,
`1/("A"_"t"^4) = 2 + 1.5 xx 10^-3` t
The rate of disappearance of [A] is ____ × 10-2 M/sec when [A] = 2 M.
[Given: [At] in M and t in sec.]
[Express your answer in terms of 10-2 M /s]
[Round off your answer if required]
