Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
For a reaction : 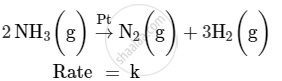
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
Solution
(i) This reaction is catalysed by Pt at high pressure. So, it is a zero-order reaction with molecularity 2.
(ii) The rate law expression for this reaction is
Rate = k
Hence, the unit of k is mol L−1 s−1.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a first order reaction x → y, 40% of the given sample of compound remains unreacted in 45 minutes. Calculate rate constant of the reaction.
For the reaction: \[\ce{2A + B → A2B}\] the rate = k[A][B]2 with k = 2.0 × 10−6 mol−2 L2 s−1. Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0.1 mol L−1, [B] = 0.2 mol L−1. Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L−1.
Write the principle behind the following methods of refining:
Hydraulic washing
In a reaction if the concentration of reactant A is tripled, the rate of reaction becomes twenty seven times. What is the order of the reaction?
For a first order A → B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 m is found to be 2.0 × 10–5. The half-life period of reaction.
For reaction 2A + B → BC + D which of the following does not Express the reaction rates
For the reaction, \[\ce{A +2B → AB2}\], the order w.r.t. reactant A is 2 and w.r.t. reactant B. What will be change in rate of reaction if the concentration of A is doubled and B is halved?
For a chemical reaction starting with some initial concentration of reactant At as a function of time (t) is given by the equation,
`1/("A"_"t"^4) = 2 + 1.5 xx 10^-3` t
The rate of disappearance of [A] is ____ × 10-2 M/sec when [A] = 2 M.
[Given: [At] in M and t in sec.]
[Express your answer in terms of 10-2 M /s]
[Round off your answer if required]
Which of the following statement is true?
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is reduced to half?
