Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write the principle behind the following methods of refining:
Hydraulic washing
Solution
The principle behind the given methods of refining are:
i) Hydraulic Washing:
This method is based on difference of gravity between ores and gangue. An upward stream of water is used to wash the powdered ore. The lighter gangue particles are washed away, leaving behind the heavier ones.
ii) Vapour-phase refining:
Vapour-phase refining is the process of refining metal by converting it into its volatile compound and then, decomposing it to obtain a pure metal. To carry out this process,
(i) the metal should form a volatile compound with an available reagent.
(ii) the volatile compound should be easily decomposable, so that the metal can be easily recovered. This method is used for refining nickel, zirconium and titanium.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
(i) Write the differential rate equation.
(ii) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of A three times?
(iii) How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
What is pseudo first order reaction? Give one· example of it.
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
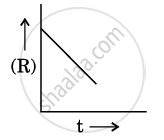
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume :
SO2Cl2 (g) → SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
| Experiment | Time/s–1 | Total pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.7 |
Calculate the rate constant.
(Given : log 4 = 0.6021, log 2 = 0.3010)
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
Rate law for the reaction \[\ce{A + 2B -> C}\] is found to be Rate = k [A][B]. Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be ______.
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?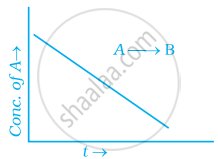
Why is the probability of reaction with molecularity higher than three very rare?
Match the graph given in Column I with the order of reaction given in Column II. More than one item in Column I may link to the same item of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) |  |
|
| (ii) |  |
(a) 1st order |
| (iii) |  |
(b) Zero-order |
| (iv) |  |
For a first order A → B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 m is found to be 2.0 × 10–5. The half-life period of reaction.
