Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
(i) Write the differential rate equation.
(ii) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of A three times?
(iii) How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
Solution
(i) A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
Differential rate equation:− `Rate=(-d[R])/dt=K[A]^2[B]`
(ii) On increasing the concentration of A three times i.e. 3A:
`Rate=k[3A]^2[B]=9k[A]^2[B]=9k[A]^2[B]=9(Rate)` , i.e. 9 times the initial rate.
(iii) On increasing the concentration of A and B as 2A and 2B:
`Rate=k[2A],^2[2B]=k(4xx2) i.e. 8 times the initial rate.[A]^2[B]=8k[A]^2[B]=8(Rate)` i.e. 8 times the initial rate
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write two factors that affect the rate of reaction.
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of B is doubled?
For a reaction : 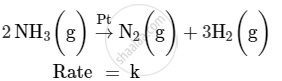
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of B three times?
Write resonating structures of ozone.
Which of the following statement is true for order of a reaction?
Rate law for the reaction \[\ce{A + 2B -> C}\] is found to be Rate = k [A][B]. Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be ______.
For a complex reaction:
(i) order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
(ii) order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
(iii) order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
(iv) molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non interger.
For which type of reactions, order and molecularity have the same value?
Use Molecular Orbital theory to determine the bond order in each of species, [He2j+ and [He2]2+?
