Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
(i) Write the differential rate equation.
(ii) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of A three times?
(iii) How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
उत्तर
(i) A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
Differential rate equation:− `Rate=(-d[R])/dt=K[A]^2[B]`
(ii) On increasing the concentration of A three times i.e. 3A:
`Rate=k[3A]^2[B]=9k[A]^2[B]=9k[A]^2[B]=9(Rate)` , i.e. 9 times the initial rate.
(iii) On increasing the concentration of A and B as 2A and 2B:
`Rate=k[2A],^2[2B]=k(4xx2) i.e. 8 times the initial rate.[A]^2[B]=8k[A]^2[B]=8(Rate)` i.e. 8 times the initial rate
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is pseudo first order reaction? Give one· example of it.
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume :
SO2Cl2 (g) → SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
| Experiment | Time/s–1 | Total pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.7 |
Calculate the rate constant.
(Given : log 4 = 0.6021, log 2 = 0.3010)
How does calcination differ from roasting?
Define the following terms:
Pseudo first-order reaction
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?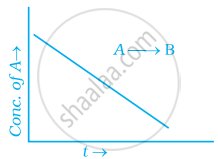
Why can we not determine the order of a reaction by taking into consideration the balanced chemical equation?
Match the graph given in Column I with the order of reaction given in Column II. More than one item in Column I may link to the same item of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) |  |
|
| (ii) |  |
(a) 1st order |
| (iii) |  |
(b) Zero-order |
| (iv) |  |
For a reaction A + B → products, the rate law is given by: r = `K[A]^(1/2)`. What is the order of reaction?
The half-life period of a. substance in a certain enzyme catalysed reaction is 138 s. The time required for the concentration of the substance to fall from 1.28 mol–1 to 0.04 mg L–1 is
