Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?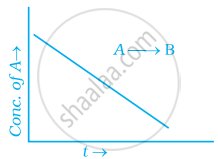
उत्तर
(i) Zero order reaction
(ii) [R] – [R]0 – kt
∴ Slope = – k
(iii) `(mol^-1L)/(s^-1)` = k[A]0 or k = mol–1 Ls–1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y?
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
What is the order of a reaction which has a rate expression; Rate = `"k"["A"]^(3/2)["B"]^1`?
Consider a first order gas phase decomposition reaction given below :
\[\ce{A(g) -> B(g) + C(g)}\]
The initial pressure of the system before decomposition of A was pi. After lapse of time ‘t’, total pressure of the system increased by x units and became ‘pt’ The rate constant k for the reaction is given as ______.
Why can’t molecularity of any reaction be equal to zero?
Assertion: Order of the reaction can be zero or fractional.
Reason: We cannot determine order from balanced chemical equation.
For a reaction A + B → products, the rate law is given by: r = `K[A]^(1/2)`. What is the order of reaction?
At concentration of 0.1 and 0.2 mol L–1 the rates of deem position of a compound were found to be 0.18 and 0.72 mol L–1 m–1. What is the order of the reaction?
