Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Assertion: The enthalpy of reaction remains constant in the presence of a catalyst.
Reason: A catalyst participating in the reaction, forms different activated complex and lowers down the activation energy but the difference in energy of reactant and product remains the same.
विकल्प
Both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Both assertion and reason are correct but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
उत्तर
Both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
AH = Activation Energy of forward reaction – Activation Energy of reverse reaction.
Catalyst does not alter heat of reaction because it affects activation energy of forward and reverse reactions equally.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
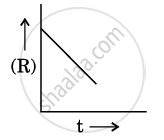
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{CH3CHO_{(g)} -> CH4_{(g)} + CO_{(g)}}\] Rate = k [CH3CHO]3/2
For a reaction R ---> P, half-life (t1/2) is observed to be independent of the initial concentration of reactants. What is the order of reaction?
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
Which of the following statement is true for order of a reaction?
Rate law for the reaction \[\ce{A + 2B -> C}\] is found to be Rate = k [A][B]. Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be ______.
Why is the probability of reaction with molecularity higher than three very rare?
Assertion: Order and molecularity are same.
Reason: Order is determined experimentally and molecularity is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficient of rate determining elementary step.
On heating compound (A) gives a gas (B) which is constituent of air. The gas when treated with H2 in the presence of catalyst gives another gas (C) which is basic in nature, (A) should not be ______.
A drop of solution (volume 0.05 ml) contains 3.0 × 10-6 mole of H+. If the rate constant of disappearance of H+ is 1.0 × 107 mole l-1s-1. It would take for H+ in drop to disappear in ______ × 10-9s.
