Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For a reaction R ---> P, half-life (t1/2) is observed to be independent of the initial concentration of reactants. What is the order of reaction?
उत्तर
The half-life for first order rection is independent of the initial concentration.
संबंधित प्रश्न
For the first order thermal decomposition reaction, the following data were obtained:
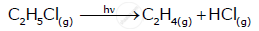
Time / sec Totalpressure / atm
0 0.30
300 0.50
Calculate the rate constant
(Given: log 2 = 0.301, log3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y?
Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
\[\ce{A(g) + 2B(g) -> 2C(g)}\]
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.
| Experiment | Initial concentration of [A]/mol L–¹ |
Initial concentration of [B]/mol L–¹ |
Initial rate of formation of [C]/mol L–¹ s–¹ |
| 1. | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2. | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
| 3. | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
In any unimolecular reaction:
(i) only one reacting species is involved in the rate determining step.
(ii) the order and the molecularity of slowest step are equal to one.
(iii) the molecularity of the reaction is one and order is zero.
(iv) both molecularity and order of the reaction are one.
Why can we not determine the order of a reaction by taking into consideration the balanced chemical equation?
For a reaction R → p the concentration of reactant change from 0.03 m to 0.02 m in minute, calculate the average rate of the reaction using the unit of second.
For a reaction 1/2 A ⇒ 2B, rate of disappearance of A is related 't o the appearance of B by the expression:
The half-life period of a. substance in a certain enzyme catalysed reaction is 138 s. The time required for the concentration of the substance to fall from 1.28 mol–1 to 0.04 mg L–1 is
Assertion (A): Order of reaction is applicable to elementary as well as complex reactions.
Reason (R): For a complex reaction, molecularity has no meaning.
Which of the following statement is true?
