Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For the first order thermal decomposition reaction, the following data were obtained:
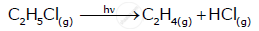
Time / sec Totalpressure / atm
0 0.30
300 0.50
Calculate the rate constant
(Given: log 2 = 0.301, log3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
उत्तर
Given :
Pi = 0.30 atm
Pt = 0.50 atm
C2H5Cl(g)→C2H4(g)+HCl(g)
Pi 0 0 (At t = 0 sec)
Pi-x x x (At t = 300 sec)
So,
Pi - x + x + x = Pt
0.3+x = 0.5
x = 0.2
Then, Pi - x = 0.3 - 0.2 = 0.1 atm
For first order reaction,
`k=2.303/tlog(P_i/(P_i-x))`
`=2.303/tlog(0.3/0.1)`
`=(2.303xxlog3)/300=(2.303xx0.4771)/300`
k = 0.0037 s-1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
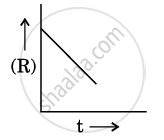
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y?
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{C2H5Cl_{(g)} -> C2H4_{(g)} + HCl_{(g)}}\] Rate = k [C2H5Cl]
For the reaction: \[\ce{2A + B → A2B}\] the rate = k[A][B]2 with k = 2.0 × 10−6 mol−2 L2 s−1. Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0.1 mol L−1, [B] = 0.2 mol L−1. Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L−1.
Define the following terms:
Pseudo first-order reaction
Assertion: Order of the reaction can be zero or fractional.
Reason: We cannot determine order from balanced chemical equation.
The role of a catalyst is to change
For a reaction \[\ce{Cl2l(g) + 2No(g) -> 2NaCl(g)}\] the rate law is expressed as rate= K[Cl2] [No]2 what is the order of the reaction?
The rate constant for the reaction \[\ce{2H2O5 -> 4NO2 + O2}\] is 30 × 10–5 sec–1. if the rate is 204 × 10–5 mol L–1 S–1, then the concentration of N2O5 (in mol–1) is-
For reaction 2A + B → BC + D which of the following does not Express the reaction rates
