Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For the first order thermal decomposition reaction, the following data were obtained:
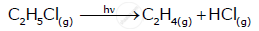
Time / sec Totalpressure / atm
0 0.30
300 0.50
Calculate the rate constant
(Given: log 2 = 0.301, log3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
उत्तर
Given :
Pi = 0.30 atm
Pt = 0.50 atm
C2H5Cl(g)→C2H4(g)+HCl(g)
Pi 0 0 (At t = 0 sec)
Pi-x x x (At t = 300 sec)
So,
Pi - x + x + x = Pt
0.3+x = 0.5
x = 0.2
Then, Pi - x = 0.3 - 0.2 = 0.1 atm
For first order reaction,
`k=2.303/tlog(P_i/(P_i-x))`
`=2.303/tlog(0.3/0.1)`
`=(2.303xxlog3)/300=(2.303xx0.4771)/300`
k = 0.0037 s-1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
(i) Write the differential rate equation.
(ii) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of A three times?
(iii) How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
For a reaction: 
Rate = k
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
For a reaction : 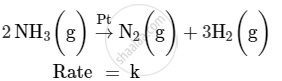
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
How does calcination differ from roasting?
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
Which of the following statements is not correct about order of a reaction.
Why is the probability of reaction with molecularity higher than three very rare?
Why can’t molecularity of any reaction be equal to zero?
Why molecularity is applicable only for elementary reactions and order is applicable for elementary as well as complex reactions?
Identify the order of reaction from the following unit for its rate constant:
L mol–1s–1
