Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why molecularity is applicable only for elementary reactions and order is applicable for elementary as well as complex reactions?
उत्तर
A complex reaction proceeds through several elementary reactions. Numbers of molecules involved in each elementary reaction may be different i.e., the molecularity of each step may be different. Therefore, discussion of molecularity of overall complex reaction is meaningless. On the other hand, order of a complex reaction is determined by the slowest step in its mechanism and is not meaningless even in the case of complex reactions.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
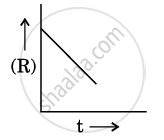
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
How does calcination differ from roasting?
Define the following terms:
Half-life period of reaction (t1/2).
In any unimolecular reaction:
(i) only one reacting species is involved in the rate determining step.
(ii) the order and the molecularity of slowest step are equal to one.
(iii) the molecularity of the reaction is one and order is zero.
(iv) both molecularity and order of the reaction are one.
Assertion: Order of the reaction can be zero or fractional.
Reason: We cannot determine order from balanced chemical equation.
Assertion: Order and molecularity are same.
Reason: Order is determined experimentally and molecularity is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficient of rate determining elementary step.
Assertion: Rate constants determined from Arrhenius equation are fairly accurate for simple as well as complex molecules.
Reason: Reactant molecules undergo chemical change irrespective of their orientation during collision.
The conversion of molecules A to B follow second order kinetics. If concentration of A is increased to three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B?
On heating compound (A) gives a gas (B) which is constituent of air. The gas when treated with H2 in the presence of catalyst gives another gas (C) which is basic in nature, (A) should not be ______.
Assertion (A): Order of reaction is applicable to elementary as well as complex reactions.
Reason (R): For a complex reaction, molecularity has no meaning.
