Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The conversion of molecules A to B follow second order kinetics. If concentration of A is increased to three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B?
उत्तर
For the reaction A → B,
Since it follows second-order kinetics so,
Rate of reaction (r) = k[A]2 ...(1)
If the concentration of reactant increased to three times.
Rate of reaction (r') = k[3A]2 ...(2)
Thus, on dividing equations (1) and (2)
`r/r^' = (k[A]^2)/(k[3A]^2)`
= `1/9`
Therefore, the rate of formation of B increases to 9 times.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
For a reaction : 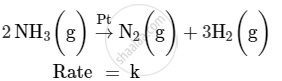
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of B three times?
Write the principle behind the following methods of refining:
Hydraulic washing
What is the order of a reaction which has a rate expression; Rate = `"k"["A"]^(3/2)["B"]^1`?
Why does the rate of any reaction generally decreases during the course of the reaction?
The role of a catalyst is to change
In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction.
For a reaction R → p the concentration of reactant change from 0.03 m to 0.02 m in minute, calculate the average rate of the reaction using the unit of second.
Which of the following statement is true?
