Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why does the rate of any reaction generally decreases during the course of the reaction?
उत्तर
The rate of a reaction depends on the concentration of reactants. As the reaction progresses, the concentration of reactants decreases because the reactants start getting converted to products. Hence the rate decreases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
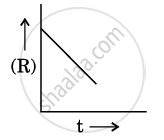
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
The decomposition of N2O5(g) at 320K according to the following equation follows first order reaction:
`N_2O_(5(g))->2NO_(2(g))+1/2O_(2(g))`
The initial concentration of N2O5(g) is 1.24 x 10-2 mol. L-1 and after 60 minutes 0.20x10-2 molL-1. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction at 320K.
For a complex reaction:
(i) order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
(ii) order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
(iii) order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
(iv) molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non interger.
In a reaction if the concentration of reactant A is tripled, the rate of reaction becomes twenty seven times. What is the order of the reaction?
The role of a catalyst is to change
For a reaction A + B → products, the rate law is given by: r = `K[A]^(1/2)`. What is the order of reaction?
Identify the order of reaction from the following unit for its rate constant:
L mol–1s–1
A drop of solution (volume 0.05 ml) contains 3.0 × 10-6 mole of H+. If the rate constant of disappearance of H+ is 1.0 × 107 mole l-1s-1. It would take for H+ in drop to disappear in ______ × 10-9s.
A flask contains a mixture of compounds A and B. Both compounds decompose by first-order kinetics. The half-lives for A and B are 300 s and 180 s, respectively. If the concentrations of A and B are equal initially, the time required for the concentration of A to be four times that of B (in s) is ______. (Use ln 2 = 0.693)
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is reduced to half?
