Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{H2O2_{( aq)} + 3I^-_{( aq)} + 2H^+ -> 2H2O_{(l)} + I^-_3}\] Rate = k[H2O2][I−]
उत्तर
Given rate = k[H2O2][I−]
Therefore, order of the reaction = 2
Dimension of k = `"Rate"/(["H"_2"O"_2]["I"^(-)])`
= `("mol L"^(-1) "s"^(-1))/(("mol L"^(-1))("mol L"^(-1)))`
= L mol−1 s−1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define “zero order reaction”.
Write molecularity of the following reaction:
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g)
For a reaction: 
Rate = k
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
For the first order thermal decomposition reaction, the following data were obtained:
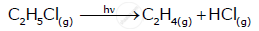
Time / sec Totalpressure / atm
0 0.30
300 0.50
Calculate the rate constant
(Given: log 2 = 0.301, log3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
For the reaction: \[\ce{2A + B → A2B}\] the rate = k[A][B]2 with k = 2.0 × 10−6 mol−2 L2 s−1. Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0.1 mol L−1, [B] = 0.2 mol L−1. Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L−1.
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of B three times?
The decomposition of N2O5(g) at 320K according to the following equation follows first order reaction:
`N_2O_(5(g))->2NO_(2(g))+1/2O_(2(g))`
The initial concentration of N2O5(g) is 1.24 x 10-2 mol. L-1 and after 60 minutes 0.20x10-2 molL-1. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction at 320K.
Define the following terms:
Half-life period of reaction (t1/2).
Rate of reaction for the combustion of propane is equal to:
\[\ce{C3H8_{(g)} + 5O2_{(g)} -> 3CO2_{(g)} + 4H2O_{(g)}}\]
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
For which type of reactions, order and molecularity have the same value?
In a reaction if the concentration of reactant A is tripled, the rate of reaction becomes twenty seven times. What is the order of the reaction?
Match the graph given in Column I with the order of reaction given in Column II. More than one item in Column I may link to the same item of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) |  |
|
| (ii) |  |
(a) 1st order |
| (iii) |  |
(b) Zero-order |
| (iv) |  |
Assertion: Order of the reaction can be zero or fractional.
Reason: We cannot determine order from balanced chemical equation.
Use Molecular Orbital theory to determine the bond order in each of species, [He2j+ and [He2]2+?
A catalyst in a reaction changes which of the following?
The role of a catalyst is to change
For a first order A → B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 m is found to be 2.0 × 10–5. The half-life period of reaction.
For reaction 2A + B → BC + D which of the following does not Express the reaction rates
