Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How does calcination differ from roasting?
Solution
| Roasting | Calcination |
| Ore is heated in excess of air. | Ore is heated in the absence or limited supply of air. |
| This is used for sulphide ores. | This is used for carbonate ores. |
| SO2 is produced along with metal oxide. | CO2 is produced along with metal oxide. |
| e.g. \[\ce{ 2ZnS + 3O2 ->[\Delta] 2ZnO + 2SO2}\] | e.g. \[\ce{ZnCO3 ->[\Delta] ZnO + CO2}\] |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is pseudo first order reaction? Give one· example of it.
For the first order thermal decomposition reaction, the following data were obtained:
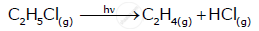
Time / sec Totalpressure / atm
0 0.30
300 0.50
Calculate the rate constant
(Given: log 2 = 0.301, log3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
For a reaction : 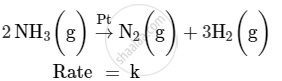
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
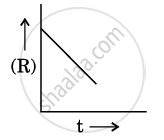
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y?
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. Write the differential rate equation.
The decomposition of N2O5(g) at 320K according to the following equation follows first order reaction:
`N_2O_(5(g))->2NO_(2(g))+1/2O_(2(g))`
The initial concentration of N2O5(g) is 1.24 x 10-2 mol. L-1 and after 60 minutes 0.20x10-2 molL-1. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction at 320K.
Define the following terms:
Half-life period of reaction (t1/2).
Which of the following statement is true for order of a reaction?
Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
\[\ce{A(g) + 2B(g) -> 2C(g)}\]
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.
| Experiment | Initial concentration of [A]/mol L–¹ |
Initial concentration of [B]/mol L–¹ |
Initial rate of formation of [C]/mol L–¹ s–¹ |
| 1. | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2. | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
| 3. | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
Consider the reaction A ⇌ B. The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
In any unimolecular reaction:
(i) only one reacting species is involved in the rate determining step.
(ii) the order and the molecularity of slowest step are equal to one.
(iii) the molecularity of the reaction is one and order is zero.
(iv) both molecularity and order of the reaction are one.
For a complex reaction:
(i) order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
(ii) order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
(iii) order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
(iv) molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non interger.
Why is the probability of reaction with molecularity higher than three very rare?
Why molecularity is applicable only for elementary reactions and order is applicable for elementary as well as complex reactions?
Why can we not determine the order of a reaction by taking into consideration the balanced chemical equation?
For a reaction R → p the concentration of reactant change from 0.03 m to 0.02 m in minute, calculate the average rate of the reaction using the unit of second.
For a first order A → B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 m is found to be 2.0 × 10–5. The half-life period of reaction.
For reaction 2A + B → BC + D which of the following does not Express the reaction rates
At concentration of 0.1 and 0.2 mol L–1 the rates of deem position of a compound were found to be 0.18 and 0.72 mol L–1 m–1. What is the order of the reaction?
Identify the order of reaction from the following unit for its rate constant:
L mol–1s–1
A flask contains a mixture of compounds A and B. Both compounds decompose by first-order kinetics. The half-lives for A and B are 300 s and 180 s, respectively. If the concentrations of A and B are equal initially, the time required for the concentration of A to be four times that of B (in s) is ______. (Use ln 2 = 0.693)
Assertion (A): Order of reaction is applicable to elementary as well as complex reactions.
Reason (R): For a complex reaction, molecularity has no meaning.
