Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. Write the differential rate equation.
Solution
The differential rate equation will be
`(dx)/dt = k[A][B]^2`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A → B is a first order reaction with rate 6.6 × 10-5m-s-1. When [A] is 0.6m, rate constant of the reaction is
- 1.1 × 10-5s-1
- 1.1 × 10-4s-1
- 9 × 10-5s-1
- 9 × 10-4s-1
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
For the reaction: \[\ce{2A + B → A2B}\] the rate = k[A][B]2 with k = 2.0 × 10−6 mol−2 L2 s−1. Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0.1 mol L−1, [B] = 0.2 mol L−1. Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L−1.
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of B three times?
For a reaction R ---> P, half-life (t1/2) is observed to be independent of the initial concentration of reactants. What is the order of reaction?
Define the following terms:
Pseudo first-order reaction
Rate of reaction for the combustion of propane is equal to:
\[\ce{C3H8_{(g)} + 5O2_{(g)} -> 3CO2_{(g)} + 4H2O_{(g)}}\]
What is the order of a reaction which has a rate expression; Rate = `"k"["A"]^(3/2)["B"]^1`?
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
Which of the following statements is not correct about order of a reaction.
Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
\[\ce{A(g) + 2B(g) -> 2C(g)}\]
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.
| Experiment | Initial concentration of [A]/mol L–¹ |
Initial concentration of [B]/mol L–¹ |
Initial rate of formation of [C]/mol L–¹ s–¹ |
| 1. | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2. | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
| 3. | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
For a complex reaction:
(i) order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
(ii) order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
(iii) order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
(iv) molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non interger.
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?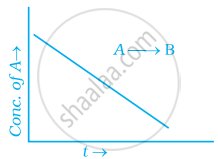
The rate of a chemical reaction double for every 10° rise in temperature. If the temperature is raised. by 50°C, the rate of relation by about:-
If the 0.05 molar solution of m+ is replaced by a 0.0025 molar m+ solution, then the magnitude of the cell potential would be
For reaction 2A + B → BC + D which of the following does not Express the reaction rates
At concentration of 0.1 and 0.2 mol L–1 the rates of deem position of a compound were found to be 0.18 and 0.72 mol L–1 m–1. What is the order of the reaction?
Identify the order of reaction from the following unit for its rate constant:
L mol–1s–1
