Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. Write the differential rate equation.
उत्तर
The differential rate equation will be
`(dx)/dt = k[A][B]^2`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is pseudo first order reaction? Give one· example of it.
Write molecularity of the following reaction:
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g)
Write two factors that affect the rate of reaction.
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of B is doubled?
For a reaction : 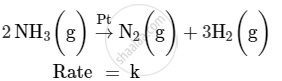
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is doubled?
In a reaction between A and B, the initial rate of reaction (r0) was measured for different initial concentrations of A and B as given below:
| A/mol L−1 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.40 |
| B/mol L−1 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| r0/mol L−1 s−1 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 1.43 × 10−4 |
What is the order of the reaction with respect to A and B?
Define the following terms:
Pseudo first-order reaction
Rate of reaction for the combustion of propane is equal to:
\[\ce{C3H8_{(g)} + 5O2_{(g)} -> 3CO2_{(g)} + 4H2O_{(g)}}\]
What is the order of a reaction which has a rate expression; Rate = `"k"["A"]^(3/2)["B"]^1`?
Consider a first order gas phase decomposition reaction given below :
\[\ce{A(g) -> B(g) + C(g)}\]
The initial pressure of the system before decomposition of A was pi. After lapse of time ‘t’, total pressure of the system increased by x units and became ‘pt’ The rate constant k for the reaction is given as ______.
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?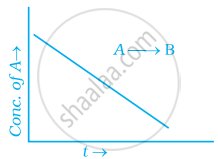
Why molecularity is applicable only for elementary reactions and order is applicable for elementary as well as complex reactions?
The role of a catalyst is to change
For a reaction A + B → products, the rate law is given by: r = `K[A]^(1/2)`. What is the order of reaction?
If the 0.05 molar solution of m+ is replaced by a 0.0025 molar m+ solution, then the magnitude of the cell potential would be
Identify the order of reaction from the following unit for its rate constant:
L mol–1s–1
A drop of solution (volume 0.05 ml) contains 3.0 × 10-6 mole of H+. If the rate constant of disappearance of H+ is 1.0 × 107 mole l-1s-1. It would take for H+ in drop to disappear in ______ × 10-9s.
