Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a reaction between A and B, the initial rate of reaction (r0) was measured for different initial concentrations of A and B as given below:
| A/mol L−1 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.40 |
| B/mol L−1 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| r0/mol L−1 s−1 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 1.43 × 10−4 |
What is the order of the reaction with respect to A and B?
उत्तर
`"dx"/"dt"` = k[A]x [B]y
5.07 × 10−5 = k(0.2)x (0.3)y ...(i)
5.07 × 10−5 = k(0.2)x (0.10)y ...(ii)
Dividing (i) by (ii), we get
1 = 3y ⇒ 30
3y ⇒ y = 0
5.07 × 10−5 = k(0.2)x (0.1)0 ...(iii)
1.43 × 10−4 = k(0.4)x (0.05)0 ...(iv)
Dividing (iv) by (iii), we get 2.8 = 2x
log 2.8 = x log 2
or x = `log2.8/log2.0`
= `0.4472/0.3010`
= 1.48
≈ 1.5
The order of reaction is 1.5 with respect to 'A' and zero with respect to 'B'.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define “zero order reaction”.
A → B is a first order reaction with rate 6.6 × 10-5m-s-1. When [A] is 0.6m, rate constant of the reaction is
- 1.1 × 10-5s-1
- 1.1 × 10-4s-1
- 9 × 10-5s-1
- 9 × 10-4s-1
What is pseudo first order reaction? Give one· example of it.
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of B is doubled?
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
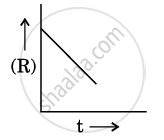
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{CH3CHO_{(g)} -> CH4_{(g)} + CO_{(g)}}\] Rate = k [CH3CHO]3/2
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
How does calcination differ from roasting?
Write resonating structures of ozone.
Write the principle behind the following methods of refining:
Hydraulic washing
What is the order of a reaction which has a rate expression; Rate = `"k"["A"]^(3/2)["B"]^1`?
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
In any unimolecular reaction:
(i) only one reacting species is involved in the rate determining step.
(ii) the order and the molecularity of slowest step are equal to one.
(iii) the molecularity of the reaction is one and order is zero.
(iv) both molecularity and order of the reaction are one.
For which type of reactions, order and molecularity have the same value?
Why does the rate of any reaction generally decreases during the course of the reaction?
Match the graph given in Column I with the order of reaction given in Column II. More than one item in Column I may link to the same item of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) |  |
|
| (ii) |  |
(a) 1st order |
| (iii) |  |
(b) Zero-order |
| (iv) |  |
Assertion: Order of the reaction can be zero or fractional.
Reason: We cannot determine order from balanced chemical equation.
For reaction 2A + B → BC + D which of the following does not Express the reaction rates
A drop of solution (volume 0.05 ml) contains 3.0 × 10-6 mole of H+. If the rate constant of disappearance of H+ is 1.0 × 107 mole l-1s-1. It would take for H+ in drop to disappear in ______ × 10-9s.
A flask contains a mixture of compounds A and B. Both compounds decompose by first-order kinetics. The half-lives for A and B are 300 s and 180 s, respectively. If the concentrations of A and B are equal initially, the time required for the concentration of A to be four times that of B (in s) is ______. (Use ln 2 = 0.693)
