Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
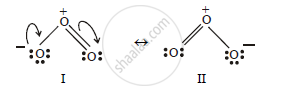
Write resonating structures of ozone.
उत्तर
Resorting structures of Ozone :
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write molecularity of the following reaction:
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g)
Write two factors that affect the rate of reaction.
For the hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution, the following results were obtained :
| t/s | 0 | 30 | 60 |
| [CH3COOCH3] / mol L–1 | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.15 |
(i) Show that it follows pseudo first order reaction, as the concentration of water remains constant.
(ii) Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time interval 30 to 60 seconds.
(Given log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021)
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
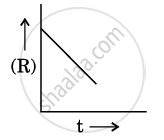
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
For a reaction, \[\ce{A + B -> Product}\]; the rate law is given by, `r = k[A]^(1/2)[B]^2`. What is the order of the reaction?
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
For the reaction: \[\ce{2A + B → A2B}\] the rate = k[A][B]2 with k = 2.0 × 10−6 mol−2 L2 s−1. Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0.1 mol L−1, [B] = 0.2 mol L−1. Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L−1.
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is doubled?
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of B three times?
The decomposition of N2O5(g) at 320K according to the following equation follows first order reaction:
`N_2O_(5(g))->2NO_(2(g))+1/2O_(2(g))`
The initial concentration of N2O5(g) is 1.24 x 10-2 mol. L-1 and after 60 minutes 0.20x10-2 molL-1. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction at 320K.
Define the following terms:
Pseudo first-order reaction
Rate of reaction for the combustion of propane is equal to:
\[\ce{C3H8_{(g)} + 5O2_{(g)} -> 3CO2_{(g)} + 4H2O_{(g)}}\]
Which of the following statement is true for order of a reaction?
Consider a first order gas phase decomposition reaction given below :
\[\ce{A(g) -> B(g) + C(g)}\]
The initial pressure of the system before decomposition of A was pi. After lapse of time ‘t’, total pressure of the system increased by x units and became ‘pt’ The rate constant k for the reaction is given as ______.
Which of the following statements is not correct about order of a reaction.
For which type of reactions, order and molecularity have the same value?
Assertion: Order and molecularity are same.
Reason: Order is determined experimentally and molecularity is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficient of rate determining elementary step.
Assertion: The enthalpy of reaction remains constant in the presence of a catalyst.
Reason: A catalyst participating in the reaction, forms different activated complex and lowers down the activation energy but the difference in energy of reactant and product remains the same.
In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction.
For a reaction R → p the concentration of reactant change from 0.03 m to 0.02 m in minute, calculate the average rate of the reaction using the unit of second.
For a first order A → B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 m is found to be 2.0 × 10–5. The half-life period of reaction.
For a reaction 1/2 A ⇒ 2B, rate of disappearance of A is related 't o the appearance of B by the expression:
The number of molecules of the reactants taking part in a single step of the reaction is indicative of ______.
The conversion of molecules A to B follow second order kinetics. If concentration of A is increased to three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B?
On heating compound (A) gives a gas (B) which is constituent of air. The gas when treated with H2 in the presence of catalyst gives another gas (C) which is basic in nature, (A) should not be ______.
A flask contains a mixture of compounds A and B. Both compounds decompose by first-order kinetics. The half-lives for A and B are 300 s and 180 s, respectively. If the concentrations of A and B are equal initially, the time required for the concentration of A to be four times that of B (in s) is ______. (Use ln 2 = 0.693)
