Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For the hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution, the following results were obtained :
| t/s | 0 | 30 | 60 |
| [CH3COOCH3] / mol L–1 | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.15 |
(i) Show that it follows pseudo first order reaction, as the concentration of water remains constant.
(ii) Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time interval 30 to 60 seconds.
(Given log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021)
उत्तर
(i) For the hydrolysis of methyl acetate to be a pseudo first-order reaction, the reaction should be first order with respect to ester when [H2O] is constant. The rate constant k for a first order reaction is given by
`k=2.303/t`
where[R]o = Initial concentration of reactant
[R] = Final concentration of reactant
At t1 = 30 s,
`k_1=2.303/30`
At t2 = 60 s,
`k_2=2.303/60`
It can be seen that the rate constant k for the reaction has a constant value under any given time interval. Hence, the given reaction follows the pseudo first-order kinetics.
(ii) Average rate of reaction between the time interval of 30–60 seconds is given by
`Rate=-(Delta[R])/(Deltat)`
`=-((0.15-0.30)/(60-30))`
`=0.15/30=0.005`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a first order reaction x → y, 40% of the given sample of compound remains unreacted in 45 minutes. Calculate rate constant of the reaction.
Write two factors that affect the rate of reaction.
The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y?
Define the following terms:
Half-life period of reaction (t1/2).
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?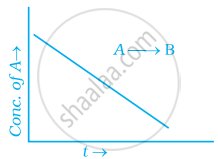
Assertion: Order and molecularity are same.
Reason: Order is determined experimentally and molecularity is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficient of rate determining elementary step.
The role of a catalyst is to change
The rate of a chemical reaction double for every 10° rise in temperature. If the temperature is raised. by 50°C, the rate of relation by about:-
The conversion of molecules A to B follow second order kinetics. If concentration of A is increased to three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B?
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is reduced to half?
