Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In a pseudo first order hydrolysis of ester in water, the following results were obtained:
| t/s | 0 | 30 | 60 | 90 |
| [A]/mol L−1 | 0.55 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.085 |
Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time interval 30 to 60 seconds.
Solution
Average rate of reaction between the time interval, 30 to 60 seconds = `("C"_2 - "C"_1)/("t"_2 - "t"_1)`
= `(0.17 - 0.31)/(60 - 30)`
= `0.14/30`
= 4.67 × 10−3 mol L−1 s−1
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Sucrose decomposes in acid solution into glucose and fructose according to the first order rate law with `"t"_(1/2)`= 3 hours. What fraction of the sample of sucrose remains after 8 hours?
A first order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10−3 s−1. How long will 5 g of this reactant take to reduce to 3 g?
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume.
\[\ce{SO2Cl2_{(g)} -> SO2_{(g)} + Cl2_{(g)}}\]
| Experiment | Time/s–1 | Total pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.6 |
Calculate the rate of the reaction when total pressure is 0.65 atm.
For the decomposition of azoisopropane to hexane and nitrogen at 543 K, the following data are obtained.
| t (sec) | P(mm of Hg) |
| 0 | 35.0 |
| 360 | 54.0 |
| 720 | 63.0 |
Calculate the rate constant.
A first order reaction takes 20 minutes for 25% decomposition. Calculate the time when 75% of the reaction will be completed.
(Given : log = 2 = 0·3010, log 3 = 0·4771, log 4 = 0·6021)
Define order of reaction. How does order of a reaction differ from molecularity for a complex reaction?
A first order reaction is 50% completed in 1.26 × 1014 s. How much time would it take for 100% completion?
Which of the following graphs is correct for a first order reaction?

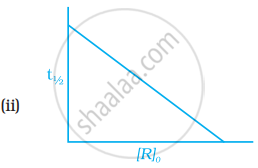
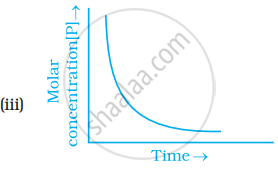
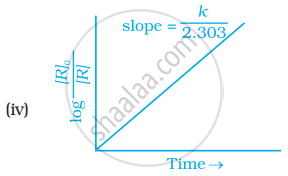
State a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order reaction.
With the help of an example explain what is meant by pseudo first order reaction.
In the presence of acid, the initial concentration of cane sugar was reduced from 0.2 M to 0.1 Min 5 hours and to 0.05 Min 10 hours. The reaction must be of?
The rate constant of a first order reaction is 6.9 × 10–3s–1. How much time will it take to reduce the initial concentration to its 1/8th value?
The decomposition of formic acid on gold surface follows first-order kinetics. If the rate constant at 300 K is 1.0 × 10−3 s−1 and the activation energy Ea = 11.488 kJ mol−1, the rate constant at 200 K is ______ × 10−5 s−1. (Round off to the Nearest Integer)
(Given R = 8.314 J mol−1 K−1)
The reaction \[\ce{SO2Cl2(g) -> SO2(g) + Cl2(g)}\] is a first-order gas reaction with k = 2.2 × 10−5 sec−1 at 320°C. The percentage of SO2Cl2 is decomposed on heating this gas for 90 min, is ______%.
For a first order reaction, the ratio of the time for 75% completion of a reaction to the time for 50% completion is ______. (Integer answer)
The slope in the plot of ln[R] vs. time for a first order reaction is ______.
Define first-order reaction.
Slove: \[\ce{2NOBr -> 2NO_{2(g)} + Br_{2(g)}}\]
For the above reaction, the rate law is rate = k[NOBr]2. If the rate of reaction is 6.5 × 10−6 mol L−1 s−1 at 2 × 10−3 mol L−1 concentration of NOBr, calculate the rate constant k for the reaction.
Write the equation for integrated rate law for a first order reaction.
