Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume.
\[\ce{SO2Cl2_{(g)} -> SO2_{(g)} + Cl2_{(g)}}\]
| Experiment | Time/s–1 | Total pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.6 |
Calculate the rate of the reaction when total pressure is 0.65 atm.
Solution
The thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume is represented by the following equation.
\[\ce{SO2Cl2_{(g)} -> SO2_{(g)} + Cl2_{(g)}}\]
| At t = 0 | P0 | 0 | 0 |
| At t = t | P0 − p | p | p |
After time t, total pressure, Pt = (P0 − p) + p + p
⇒ Pt = (P0 + p)
⇒ p = Pt − P0
∴ P0 − p = P0 − (Pt − P0)
= 2 P0 − Pt
For a first order reaction,
k = `2.303/"t" log "P"_0/("P"_0 - "p")`
When t = 100 s, k = `2.303/(100s)log 0.5/(2 xx 0.5 - 0.6)`
When Pt = 0.65 atm,
P0 + p = 0.65
⇒ p = 0.65 − P0
= 0.65 − 0.5
= 0.15 atm
∴ When the total pressure is 0.65 atm, pressure of SOCl2 is \[\ce{P_{SO_2Cl_2}}\] = P0 − p
= 0.5 − 0.15
= 0.35 atm
∴ The rate of equation, when total pressure is 0.65 atm, is given by,
Rate = \[\ce{k(P_{SO_2Cl_2)}}\]
= (2.23 × 10−3 s−1) × (0.35 atm)
= 7.8 × 10−4 atm s−1
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Sucrose decomposes in acid solution into glucose and fructose according to the first order rate law with `"t"_(1/2)`= 3 hours. What fraction of the sample of sucrose remains after 8 hours?
Time required to decompose SO2Cl2 to half of its initial amount is 60 minutes. If the decomposition is a first order reaction, calculate the rate constant of the reaction.
In a pseudo first order hydrolysis of ester in water, the following results were obtained:
| t/s | 0 | 30 | 60 | 90 |
| [A]/mol L−1 | 0.55 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.085 |
Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time interval 30 to 60 seconds.
The time required for 10% completion of a first order reaction at 298 K is equal to that required for its 25% completion at 308 K. If the value of A is 4 × 1010 s−1. Calculate k at 318 K and Ea.
In the presence of acid, the initial concentration of cane sugar was reduced from 0.2 M to 0.1 Min 5 hours and to 0.05 Min 10 hours. The reaction must be of?
The rate constant of a first order reaction is 6.9 × 10–3s–1. How much time will it take to reduce the initial concentration to its 1/8th value?
First order reaction is 50% complete in 1.26 × 1014s. How much time could it take for 100% completion?
In the first order reaction, half of the reaction is complete in 100 seconds. The time for 99% of the reaction to occurs will be
The reaction X → product
Follow first order of kinetics. In 40 minutes the concentration of 'X' changes from 0.1 m to 0.025. M. The rate of reaction when concentration of X is 0.01 m is.
In a first order reaction the concentration of reactants decreases from 400mol L-1 to 25 mol L-1 in 200 seconds. The rate constant for the reaction is ______.
Observe the graph shown in figure and answer the following questions:
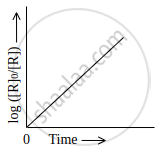
- What is the order of the reaction?
- What is the slope of the curve?
- Write the relationship between k and t1/2 (half life period).
Gaseous cyclobutene isomerizes to butadiene in a first order process which has a 'k' value of 3.3 × 10−4 s−1 at 153°C. The time in minutes it takes for the isomerization to proceed 40% to completion at this temperature is ______. (Rounded-off to the nearest integer)
For a first order reaction, the ratio of the time for 75% completion of a reaction to the time for 50% completion is ______. (Integer answer)
The slope in the plot of ln[R] vs. time for a first order reaction is ______.
Radioactive decay follows first-order kinetics. The initial amount of two radioactive elements X and Y is 1 gm each. What will be the ratio of X and Y after two days if their half-lives are 12 hours and 16 hours respectively?
Define first-order reaction.
The rate constant for the reaction:
\[\ce{2N2O_{(s)} ->2N2O4_{(g)}}\] is 4.98 × 10-4 s-1.
The order of the reaction is ______.
Show that `t_(1/2)= 0.693/k` for first reaction.
Write the unit of rate constant [k] for the first order reaction.
