Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The decomposition of N2O5(g) at 320K according to the following equation follows first order reaction:
`N_2O_(5(g))->2NO_(2(g))+1/2O_(2(g))`
The initial concentration of N2O5(g) is 1.24 x 10-2 mol. L-1 and after 60 minutes 0.20x10-2 molL-1. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction at 320K.
Solution
Data: `N_2O_(5(g))->2NO_(2(g))+1/2O_2`
`[N_2O_5]_@=1.24xx10^-2molL^-1`
`[N_2O_5]_t=0.20xx10^-2molL^-1`
k=? t=60min
Solution :
`k=2.303/t log""([N_2O_5])/([N_2O_5])`
`k=2.303/60log""((1.24xx10^-2))/((0.2xx10^-2))`
k=0.0383x0.7924
k= 0.303min-1
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a first order reaction x → y, 40% of the given sample of compound remains unreacted in 45 minutes. Calculate rate constant of the reaction.
Write molecularity of the following reaction:
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g)
For the first order thermal decomposition reaction, the following data were obtained:
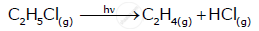
Time / sec Totalpressure / atm
0 0.30
300 0.50
Calculate the rate constant
(Given: log 2 = 0.301, log3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of B is doubled?
The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y?
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{C2H5Cl_{(g)} -> C2H4_{(g)} + HCl_{(g)}}\] Rate = k [C2H5Cl]
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
For a reaction R ---> P, half-life (t1/2) is observed to be independent of the initial concentration of reactants. What is the order of reaction?
Write the principle behind the following methods of refining:
Hydraulic washing
Define the following terms:
Half-life period of reaction (t1/2).
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
Which of the following statement is true for order of a reaction?
Consider a first order gas phase decomposition reaction given below :
\[\ce{A(g) -> B(g) + C(g)}\]
The initial pressure of the system before decomposition of A was pi. After lapse of time ‘t’, total pressure of the system increased by x units and became ‘pt’ The rate constant k for the reaction is given as ______.
Which of the following statements is not correct about order of a reaction.
The value of rate constant of a pseudo first order reaction ______.
Consider the reaction A ⇌ B. The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
For a complex reaction:
(i) order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
(ii) order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
(iii) order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
(iv) molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non interger.
In a reaction if the concentration of reactant A is tripled, the rate of reaction becomes twenty seven times. What is the order of the reaction?
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?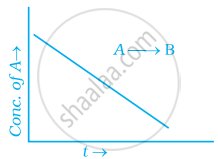
Match the graph given in Column I with the order of reaction given in Column II. More than one item in Column I may link to the same item of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) |  |
|
| (ii) |  |
(a) 1st order |
| (iii) |  |
(b) Zero-order |
| (iv) |  |
In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction.
The rate constant for the reaction \[\ce{2H2O5 -> 4NO2 + O2}\] is 30 × 10–5 sec–1. if the rate is 204 × 10–5 mol L–1 S–1, then the concentration of N2O5 (in mol–1) is-
For a first order A → B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 m is found to be 2.0 × 10–5. The half-life period of reaction.
If the 0.05 molar solution of m+ is replaced by a 0.0025 molar m+ solution, then the magnitude of the cell potential would be
The conversion of molecules A to B follow second order kinetics. If concentration of A is increased to three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B?
A drop of solution (volume 0.05 ml) contains 3.0 × 10-6 mole of H+. If the rate constant of disappearance of H+ is 1.0 × 107 mole l-1s-1. It would take for H+ in drop to disappear in ______ × 10-9s.
For a chemical reaction starting with some initial concentration of reactant At as a function of time (t) is given by the equation,
`1/("A"_"t"^4) = 2 + 1.5 xx 10^-3` t
The rate of disappearance of [A] is ____ × 10-2 M/sec when [A] = 2 M.
[Given: [At] in M and t in sec.]
[Express your answer in terms of 10-2 M /s]
[Round off your answer if required]
Assertion (A): Order of reaction is applicable to elementary as well as complex reactions.
Reason (R): For a complex reaction, molecularity has no meaning.
