Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write molecularity of the following reaction:
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g)
Solution 1
2NO+O2→2NO2
Molecularity of reaction = 3
Solution 2
The molecularity of the reaction is 3.
Explanation :
Molecularity : It is defined as the total number of reactant molecules taking part in the balanced equation of a reaction. It is a theoretical concept.
The given balanced chemical reaction is,
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g)
In this reaction, 2 NO molecules reacts with the 1 Oxygen molecule.Total number of reactant molecule = 2 + 1 = 3
Therefore, the molecularity of the reaction is 3.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define “zero order reaction”.
For a reaction: 
Rate = k
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of B is doubled?
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume :
SO2Cl2 (g) → SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
| Experiment | Time/s–1 | Total pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.7 |
Calculate the rate constant.
(Given : log 4 = 0.6021, log 2 = 0.3010)
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{H2O2_{( aq)} + 3I^-_{( aq)} + 2H^+ -> 2H2O_{(l)} + I^-_3}\] Rate = k[H2O2][I−]
How does calcination differ from roasting?
Define the following terms:
Half-life period of reaction (t1/2).
Which of the following statements is not correct about order of a reaction.
Rate law for the reaction \[\ce{A + 2B -> C}\] is found to be Rate = k [A][B]. Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be ______.
In any unimolecular reaction:
(i) only one reacting species is involved in the rate determining step.
(ii) the order and the molecularity of slowest step are equal to one.
(iii) the molecularity of the reaction is one and order is zero.
(iv) both molecularity and order of the reaction are one.
For which type of reactions, order and molecularity have the same value?
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?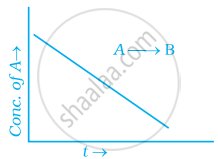
Why can’t molecularity of any reaction be equal to zero?
Match the graph given in Column I with the order of reaction given in Column II. More than one item in Column I may link to the same item of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) |  |
|
| (ii) |  |
(a) 1st order |
| (iii) |  |
(b) Zero-order |
| (iv) |  |
Assertion: Order and molecularity are same.
Reason: Order is determined experimentally and molecularity is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficient of rate determining elementary step.
The role of a catalyst is to change
In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction.
For a reaction A + B → products, the rate law is given by: r = `K[A]^(1/2)`. What is the order of reaction?
For a reaction 1/2 A ⇒ 2B, rate of disappearance of A is related 't o the appearance of B by the expression:
At concentration of 0.1 and 0.2 mol L–1 the rates of deem position of a compound were found to be 0.18 and 0.72 mol L–1 m–1. What is the order of the reaction?
For the reaction, \[\ce{A +2B → AB2}\], the order w.r.t. reactant A is 2 and w.r.t. reactant B. What will be change in rate of reaction if the concentration of A is doubled and B is halved?
Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow:
|
The rate of reaction is concerned with decrease in the concentration of reactants or increase in the concentration of products per unit of time. It can be expressed as instantaneous rate at a particular instant of time and average rate over a large interval of time. A number of factors such as temperature, concentration of reactants, catalyst affect the rate of reaction. Mathematical representation of rate of a reaction is given by rate law: Rate = k[A]x [B]y x and y indicate how sensitive the rate is to change in concentration of A and B. Sum of x + y gives the overall order of a reaction. |
- What is the effect of temperature on the rate constant of a reason? [1]
- For a reaction \[\ce{A + B → Product}\], the rate law is given by, Rate = k[A]2 [B]1/2. What is the order of the reaction? [1]
- How order and molecularity are different for complex reactions? [1]
- A first-order reaction has a rate constant 2 × 10–3 s–1. How long will 6 g of this reactant take to reduce to 2 g? [2]
OR
The half-life for radioactive decay of 14C is 6930 years. An archaeological artifact containing wood had only 75% of the 14C found in a living tree. Find the age of the sample.
[log 4 = 0.6021, log 3 = 0.4771, log 2 = 0.3010, log 10 = 1] [2]
The following data was obtained for chemical reaction given below at 975 K.
\[\ce{2NO(g) + 2H2(g) -> N2(g) + 2H2O(g)}\]
| [NO] | [H2] | Rate | |
| Mol L-1 | Mol L-1 | Mol L-1 s-1 | |
| (1) | 8 × 10-5 | 8 × 10-5 | 7 × 10-9 |
| (2) | 24 × 10-5 | 8 × 10-5 | 2.1 × 10-8 |
| (3) | 24 × 10-5 | 32 × 10-5 | 8.4 × 10-8 |
The order of the reaction with respect to NO is ______. (Integer answer)
A drop of solution (volume 0.05 ml) contains 3.0 × 10-6 mole of H+. If the rate constant of disappearance of H+ is 1.0 × 107 mole l-1s-1. It would take for H+ in drop to disappear in ______ × 10-9s.
For a chemical reaction starting with some initial concentration of reactant At as a function of time (t) is given by the equation,
`1/("A"_"t"^4) = 2 + 1.5 xx 10^-3` t
The rate of disappearance of [A] is ____ × 10-2 M/sec when [A] = 2 M.
[Given: [At] in M and t in sec.]
[Express your answer in terms of 10-2 M /s]
[Round off your answer if required]
A flask contains a mixture of compounds A and B. Both compounds decompose by first-order kinetics. The half-lives for A and B are 300 s and 180 s, respectively. If the concentrations of A and B are equal initially, the time required for the concentration of A to be four times that of B (in s) is ______. (Use ln 2 = 0.693)
Which of the following statement is true?
