Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{C2H5Cl_{(g)} -> C2H4_{(g)} + HCl_{(g)}}\] Rate = k [C2H5Cl]
Solution
Given rate = k [C2H5Cl]
Therefore, order of the reaction = 1
Dimension of k = `"Rate"/["C"_2"H"_5"Cl"]`
= `("mol L"^(-1) "s"^(-1))/"mol L"^(-1)`
= s−1
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define “zero order reaction”.
Write molecularity of the following reaction:
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g)
For the first order thermal decomposition reaction, the following data were obtained:
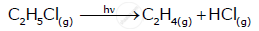
Time / sec Totalpressure / atm
0 0.30
300 0.50
Calculate the rate constant
(Given: log 2 = 0.301, log3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of B is doubled?
For a reaction : 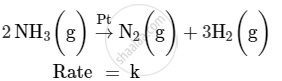
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
For a reaction, \[\ce{A + B -> Product}\]; the rate law is given by, `r = k[A]^(1/2)[B]^2`. What is the order of the reaction?
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
Write the principle behind the following methods of refining:
Hydraulic washing
Define the following terms:
Half-life period of reaction (t1/2).
Rate law for the reaction \[\ce{A + 2B -> C}\] is found to be Rate = k [A][B]. Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be ______.
Why is the probability of reaction with molecularity higher than three very rare?
For a reaction A + B → products, the rate law is given by: r = `K[A]^(1/2)`. What is the order of reaction?
For a reaction 1/2 A ⇒ 2B, rate of disappearance of A is related 't o the appearance of B by the expression:
For reaction 2A + B → BC + D which of the following does not Express the reaction rates
For the reaction, \[\ce{A +2B → AB2}\], the order w.r.t. reactant A is 2 and w.r.t. reactant B. What will be change in rate of reaction if the concentration of A is doubled and B is halved?
Identify the order of reaction from the following unit for its rate constant:
L mol–1s–1
On heating compound (A) gives a gas (B) which is constituent of air. The gas when treated with H2 in the presence of catalyst gives another gas (C) which is basic in nature, (A) should not be ______.
For a chemical reaction starting with some initial concentration of reactant At as a function of time (t) is given by the equation,
`1/("A"_"t"^4) = 2 + 1.5 xx 10^-3` t
The rate of disappearance of [A] is ____ × 10-2 M/sec when [A] = 2 M.
[Given: [At] in M and t in sec.]
[Express your answer in terms of 10-2 M /s]
[Round off your answer if required]
