Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
For a reaction, \[\ce{A + B -> Product}\]; the rate law is given by, `r = k[A]^(1/2)[B]^2`. What is the order of the reaction?
Solution
The order of the reaction = `1/2+2`
= `2 1/2`
= 2.5
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
(i) Write the differential rate equation.
(ii) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of A three times?
(iii) How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
What is pseudo first order reaction? Give one· example of it.
For the first order thermal decomposition reaction, the following data were obtained:
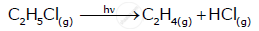
Time / sec Totalpressure / atm
0 0.30
300 0.50
Calculate the rate constant
(Given: log 2 = 0.301, log3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{CH3CHO_{(g)} -> CH4_{(g)} + CO_{(g)}}\] Rate = k [CH3CHO]3/2
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. Write the differential rate equation.
How does calcination differ from roasting?
Write resonating structures of ozone.
Write the principle behind the following methods of refining:
Hydraulic washing
Why can’t molecularity of any reaction be equal to zero?
Why can we not determine the order of a reaction by taking into consideration the balanced chemical equation?
Match the graph given in Column I with the order of reaction given in Column II. More than one item in Column I may link to the same item of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) |  |
|
| (ii) |  |
(a) 1st order |
| (iii) |  |
(b) Zero-order |
| (iv) |  |
Assertion: Order and molecularity are same.
Reason: Order is determined experimentally and molecularity is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficient of rate determining elementary step.
For a first order A → B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 m is found to be 2.0 × 10–5. The half-life period of reaction.
For the reaction, \[\ce{A +2B → AB2}\], the order w.r.t. reactant A is 2 and w.r.t. reactant B. What will be change in rate of reaction if the concentration of A is doubled and B is halved?
The conversion of molecules A to B follow second order kinetics. If concentration of A is increased to three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B?
A flask contains a mixture of compounds A and B. Both compounds decompose by first-order kinetics. The half-lives for A and B are 300 s and 180 s, respectively. If the concentrations of A and B are equal initially, the time required for the concentration of A to be four times that of B (in s) is ______. (Use ln 2 = 0.693)
Which of the following statement is true?
