Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is pseudo first order reaction? Give one· example of it.
उत्तर
A reaction which has higher order true rate law but experimentally found to behave as first order are called pseudo first order reaction.
e.g. `C_12H_22O_(11(aq))+H_2OrarrC_6H_12O_6+C_6H_12O_6`
Sucrose Glucose fractose
is an example of pseudo first order reaction, because water takes part in the reaction the true rate law
rate = k'[C12H22O11][H2O]
indicates that the reaction must be second order. Similarly to the hydrolysis of ester,[H2O] is constant and
the rate law became
rate=k[C12H22O11]
Thus, the second order true law is converted, to first order rate law.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define “zero order reaction”.
In a first order reaction x → y, 40% of the given sample of compound remains unreacted in 45 minutes. Calculate rate constant of the reaction.
A → B is a first order reaction with rate 6.6 × 10-5m-s-1. When [A] is 0.6m, rate constant of the reaction is
- 1.1 × 10-5s-1
- 1.1 × 10-4s-1
- 9 × 10-5s-1
- 9 × 10-4s-1
For the first order thermal decomposition reaction, the following data were obtained:
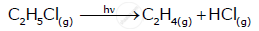
Time / sec Totalpressure / atm
0 0.30
300 0.50
Calculate the rate constant
(Given: log 2 = 0.301, log3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
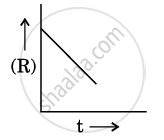
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{CH3CHO_{(g)} -> CH4_{(g)} + CO_{(g)}}\] Rate = k [CH3CHO]3/2
For the reaction: \[\ce{2A + B → A2B}\] the rate = k[A][B]2 with k = 2.0 × 10−6 mol−2 L2 s−1. Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0.1 mol L−1, [B] = 0.2 mol L−1. Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L−1.
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B. How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
The decomposition of N2O5(g) at 320K according to the following equation follows first order reaction:
`N_2O_(5(g))->2NO_(2(g))+1/2O_(2(g))`
The initial concentration of N2O5(g) is 1.24 x 10-2 mol. L-1 and after 60 minutes 0.20x10-2 molL-1. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction at 320K.
Rate of reaction for the combustion of propane is equal to:
\[\ce{C3H8_{(g)} + 5O2_{(g)} -> 3CO2_{(g)} + 4H2O_{(g)}}\]
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
Which of the following statement is true for order of a reaction?
Rate law for the reaction \[\ce{A + 2B -> C}\] is found to be Rate = k [A][B]. Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be ______.
In any unimolecular reaction:
(i) only one reacting species is involved in the rate determining step.
(ii) the order and the molecularity of slowest step are equal to one.
(iii) the molecularity of the reaction is one and order is zero.
(iv) both molecularity and order of the reaction are one.
For which type of reactions, order and molecularity have the same value?
In a reaction if the concentration of reactant A is tripled, the rate of reaction becomes twenty seven times. What is the order of the reaction?
Use Molecular Orbital theory to determine the bond order in each of species, [He2j+ and [He2]2+?
For a reaction A + B → products, the rate law is given by: r = `K[A]^(1/2)`. What is the order of reaction?
For a reaction \[\ce{Cl2l(g) + 2No(g) -> 2NaCl(g)}\] the rate law is expressed as rate= K[Cl2] [No]2 what is the order of the reaction?
For a first order A → B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 m is found to be 2.0 × 10–5. The half-life period of reaction.
For a reaction 1/2 A ⇒ 2B, rate of disappearance of A is related 't o the appearance of B by the expression:
At concentration of 0.1 and 0.2 mol L–1 the rates of deem position of a compound were found to be 0.18 and 0.72 mol L–1 m–1. What is the order of the reaction?
The number of molecules of the reactants taking part in a single step of the reaction is indicative of ______.
Identify the order of reaction from the following unit for its rate constant:
L mol–1s–1
The conversion of molecules A to B follow second order kinetics. If concentration of A is increased to three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B?
For a chemical reaction starting with some initial concentration of reactant At as a function of time (t) is given by the equation,
`1/("A"_"t"^4) = 2 + 1.5 xx 10^-3` t
The rate of disappearance of [A] is ____ × 10-2 M/sec when [A] = 2 M.
[Given: [At] in M and t in sec.]
[Express your answer in terms of 10-2 M /s]
[Round off your answer if required]
