Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
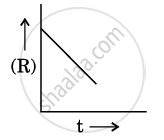
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
उत्तर १
For a chemical reaction R→P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as follows:
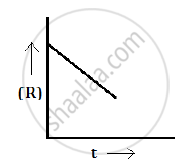
(i) The order of the reaction zero.
(ii) Slope = -k
उत्तर २
(i) The variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot shown here represents a zero order reaction, for which the rate of the reaction is proportional to zero power of the concentration of the reactants.
(ii) For a zero order reaction, rate constant is given as
`k=([R]_0-[R])/t`
So, the slope of the curve for the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is equal to the negative of the rate constant for the reaction.
उत्तर ३
(iii) Since it is a first order reaction, the unit of the rate constant is s−1.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
(i) Write the differential rate equation.
(ii) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of A three times?
(iii) How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
For the hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution, the following results were obtained :
| t/s | 0 | 30 | 60 |
| [CH3COOCH3] / mol L–1 | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.15 |
(i) Show that it follows pseudo first order reaction, as the concentration of water remains constant.
(ii) Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time interval 30 to 60 seconds.
(Given log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021)
The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y?
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is doubled?
Rate law for the reaction \[\ce{A + 2B -> C}\] is found to be Rate = k [A][B]. Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be ______.
Why does the rate of any reaction generally decreases during the course of the reaction?
For a first order A → B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 m is found to be 2.0 × 10–5. The half-life period of reaction.
Assertion (A): Order of reaction is applicable to elementary as well as complex reactions.
Reason (R): For a complex reaction, molecularity has no meaning.
Which of the following statement is true?
