Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
उत्तर
The factors that affect the rate of a reaction are as follows:
(i) Nature of the reactant - The rate of reaction depends on the nature of the reactant. For instance, ionic molecules react more quickly than covalent ones.
(ii) State of reactants - Solid reactions are slower, liquid reactions are faster, and gas reactions are very quick.
(iii) Temperature - The rate of reaction is mainly affected by temperature. Every 10°C rise in temperature leads to an increased rate of reaction by 2-3 times.
`(r_(t + 10))/r_t` = 2 − 3
This ratio is called the temperature coefficient.
There are two reasons why the rate of reaction increases with increasing temperature.
- Increasing temperature raises the average kinetic energy of reactant molecules, increasing the rate of collisions.
- As temperature rises, the number of molecules with threshold energy increases, resulting in more active molecules. As a result, the number of effective collisions grows. As a result, the rate of reaction rises.
(iv) Concentration - The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of reactants.
Rate = k × Cn, where n = order of reaction, C = concentration of reactant.
(v) Catalyst - The presence of a catalyst changes the rate of the reaction. It lowers the activation energy by producing a chemical intermediate, lowering the potential energy barrier. Thus, the rate of reaction increases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
(i) Write the differential rate equation.
(ii) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of A three times?
(iii) How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
Write two factors that affect the rate of reaction.
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume :
SO2Cl2 (g) → SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
| Experiment | Time/s–1 | Total pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.7 |
Calculate the rate constant.
(Given : log 4 = 0.6021, log 2 = 0.3010)
The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y?
For the reaction: \[\ce{2A + B → A2B}\] the rate = k[A][B]2 with k = 2.0 × 10−6 mol−2 L2 s−1. Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0.1 mol L−1, [B] = 0.2 mol L−1. Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L−1.
In a reaction between A and B, the initial rate of reaction (r0) was measured for different initial concentrations of A and B as given below:
| A/mol L−1 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.40 |
| B/mol L−1 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| r0/mol L−1 s−1 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 1.43 × 10−4 |
What is the order of the reaction with respect to A and B?
The decomposition of N2O5(g) at 320K according to the following equation follows first order reaction:
`N_2O_(5(g))->2NO_(2(g))+1/2O_(2(g))`
The initial concentration of N2O5(g) is 1.24 x 10-2 mol. L-1 and after 60 minutes 0.20x10-2 molL-1. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction at 320K.
Define the following terms:
Pseudo first-order reaction
The value of rate constant of a pseudo first order reaction ______.
For a complex reaction:
(i) order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
(ii) order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
(iii) order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
(iv) molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non interger.
For a general reaction A → B, plot of concentration of A vs time is given in figure. Answer the following question on the basis of this graph.
(i) What is the order of the reaction?
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
(iii) What are the units of rate constant?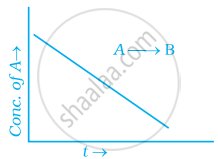
Why is the probability of reaction with molecularity higher than three very rare?
Why can’t molecularity of any reaction be equal to zero?
Why can we not determine the order of a reaction by taking into consideration the balanced chemical equation?
At concentration of 0.1 and 0.2 mol L–1 the rates of deem position of a compound were found to be 0.18 and 0.72 mol L–1 m–1. What is the order of the reaction?
The conversion of molecules A to B follow second order kinetics. If concentration of A is increased to three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B?
Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow:
|
The rate of reaction is concerned with decrease in the concentration of reactants or increase in the concentration of products per unit of time. It can be expressed as instantaneous rate at a particular instant of time and average rate over a large interval of time. A number of factors such as temperature, concentration of reactants, catalyst affect the rate of reaction. Mathematical representation of rate of a reaction is given by rate law: Rate = k[A]x [B]y x and y indicate how sensitive the rate is to change in concentration of A and B. Sum of x + y gives the overall order of a reaction. |
- What is the effect of temperature on the rate constant of a reason? [1]
- For a reaction \[\ce{A + B → Product}\], the rate law is given by, Rate = k[A]2 [B]1/2. What is the order of the reaction? [1]
- How order and molecularity are different for complex reactions? [1]
- A first-order reaction has a rate constant 2 × 10–3 s–1. How long will 6 g of this reactant take to reduce to 2 g? [2]
OR
The half-life for radioactive decay of 14C is 6930 years. An archaeological artifact containing wood had only 75% of the 14C found in a living tree. Find the age of the sample.
[log 4 = 0.6021, log 3 = 0.4771, log 2 = 0.3010, log 10 = 1] [2]
On heating compound (A) gives a gas (B) which is constituent of air. The gas when treated with H2 in the presence of catalyst gives another gas (C) which is basic in nature, (A) should not be ______.
A flask contains a mixture of compounds A and B. Both compounds decompose by first-order kinetics. The half-lives for A and B are 300 s and 180 s, respectively. If the concentrations of A and B are equal initially, the time required for the concentration of A to be four times that of B (in s) is ______. (Use ln 2 = 0.693)
