Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a reaction if the concentration of reactant A is tripled, the rate of reaction becomes twenty seven times. What is the order of the reaction?
उत्तर
Rate = `k[A]^alpha` .....(i)
27 × Rate = `k[3A]^alpha` .....(ii)
Dividing equation (ii) by equation (i), we get α = 3
∴ Order of reaction = 3
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For the hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution, the following results were obtained :
| t/s | 0 | 30 | 60 |
| [CH3COOCH3] / mol L–1 | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.15 |
(i) Show that it follows pseudo first order reaction, as the concentration of water remains constant.
(ii) Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time interval 30 to 60 seconds.
(Given log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021)
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as:
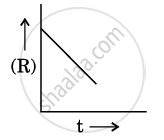
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve ?
(iii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction.
In a reaction between A and B, the initial rate of reaction (r0) was measured for different initial concentrations of A and B as given below:
| A/mol L−1 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.40 |
| B/mol L−1 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| r0/mol L−1 s−1 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 1.43 × 10−4 |
What is the order of the reaction with respect to A and B?
For a reaction R ---> P, half-life (t1/2) is observed to be independent of the initial concentration of reactants. What is the order of reaction?
Define the following terms:
Pseudo first-order reaction
Use Molecular Orbital theory to determine the bond order in each of species, [He2j+ and [He2]2+?
For a reaction R → p the concentration of reactant change from 0.03 m to 0.02 m in minute, calculate the average rate of the reaction using the unit of second.
The conversion of molecules A to B follow second order kinetics. If concentration of A is increased to three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B?
A drop of solution (volume 0.05 ml) contains 3.0 × 10-6 mole of H+. If the rate constant of disappearance of H+ is 1.0 × 107 mole l-1s-1. It would take for H+ in drop to disappear in ______ × 10-9s.
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is reduced to half?
