Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{3NO_{(g)} -> N2O_{(g)}}\] Rate = k[NO]2
उत्तर
Given rate = k[NO]2
Therefore, the order of the reaction = 2
Dimension of k = `"Rate"/["NO"]^2`
= `("mol L"^(-1) "s"^(-1))/("mol L"^(-1))^2`
= `("mol L"^(-1) "s"^(-1))/("mol"^2 "L"^(-2))`
= L mol−1 s−1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
(i) Write the differential rate equation.
(ii) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of A three times?
(iii) How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
Write two factors that affect the rate of reaction.
For a reaction : 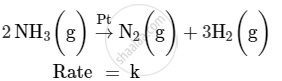
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
For the hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution, the following results were obtained :
| t/s | 0 | 30 | 60 |
| [CH3COOCH3] / mol L–1 | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.15 |
(i) Show that it follows pseudo first order reaction, as the concentration of water remains constant.
(ii) Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time interval 30 to 60 seconds.
(Given log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021)
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume :
SO2Cl2 (g) → SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
| Experiment | Time/s–1 | Total pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.7 |
Calculate the rate constant.
(Given : log 4 = 0.6021, log 2 = 0.3010)
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{C2H5Cl_{(g)} -> C2H4_{(g)} + HCl_{(g)}}\] Rate = k [C2H5Cl]
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is doubled?
How does calcination differ from roasting?
What is the order of a reaction which has a rate expression; Rate = `"k"["A"]^(3/2)["B"]^1`?
Why does the rate of any reaction generally decreases during the course of the reaction?
Why can we not determine the order of a reaction by taking into consideration the balanced chemical equation?
Match the graph given in Column I with the order of reaction given in Column II. More than one item in Column I may link to the same item of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) |  |
|
| (ii) |  |
(a) 1st order |
| (iii) |  |
(b) Zero-order |
| (iv) |  |
Assertion: Order and molecularity are same.
Reason: Order is determined experimentally and molecularity is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficient of rate determining elementary step.
Use Molecular Orbital theory to determine the bond order in each of species, [He2j+ and [He2]2+?
A catalyst in a reaction changes which of the following?
Which of the following statement is true?
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is reduced to half?
