Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
(b) Rate constant ‘k’ of a reaction varies with temperature ‘T’ according to the equation:
`logk=logA-E_a/2.303R(1/T)`
Where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for `logk Vs. 1/T` a straight line with a slope of −4250 K is obtained. Calculate ‘Ea’ for the reaction.(R = 8.314 JK−1 mol−1)
उत्तर
`log k=logA-E_a/2.303R(1/T)`
Ea → Activation energy
The above equation is like y = mx + c where if we plot y v/s x we get a straight line with slope ‘m’ and intercept ‘c’.
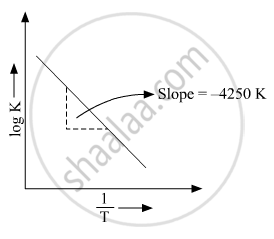
So, slope is equal to`=-E_a/2.303R`
`-E_a/2.303R=-4250k=>E_a=4250 xx 2.303 xx 8.314 =81,375.3535 j mol^(-1)`
`E_a=81.3753 KJ mol^(-1)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain a graphical method to determine activation energy of a reaction.
The rate constant for the first-order decomposition of H2O2 is given by the following equation:
`logk=14.2-(1.0xx10^4)/TK`
Calculate Ea for this reaction and rate constant k if its half-life period be 200 minutes.
(Given: R = 8.314 JK–1 mol–1)
What will be the effect of temperature on rate constant?
The rate of the chemical reaction doubles for an increase of 10 K in absolute temperature from 298 K. Calculate Ea.
Write a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order. Give an example of such a reaction. (Given : log2 = 0.3010,log 3 = 0.4771, log5 = 0.6990).
Mark the incorrect statements:
(i) Catalyst provides an alternative pathway to reaction mechanism.
(ii) Catalyst raises the activation energy.
(iii) Catalyst lowers the activation energy.
(iv) Catalyst alters enthalpy change of the reaction.
Explain how and why will the rate of reaction for a given reaction be affected when the temperature at which the reaction was taking place is decreased.
The activation energy of one of the reactions in a biochemical process is 532611 J mol–1. When the temperature falls from 310 K to 300 K, the change in rate constant observed is k300 = x × 10–3 k310. The value of x is ______.
[Given: ln 10 = 2.3, R = 8.3 J K–1 mol–1]
The equation k = `(6.5 xx 10^12 "s"^(-1))"e"^(- 26000 " K"//"T")` is followed for the decomposition of compound A. The activation energy for the reaction is ______ kJ mol-1. (Nearest integer) (Given: R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
The decomposition of N2O into N2 and O2 in the presence of gaseous argon follows second-order kinetics, with k = (5.0 × 1011 L mol−1 s−1) `"e"^(-(29000 "K")/"T")`. Arrhenius parameters are ______ kJ mol−1.
