Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(b) Rate constant ‘k’ of a reaction varies with temperature ‘T’ according to the equation:
`logk=logA-E_a/2.303R(1/T)`
Where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for `logk Vs. 1/T` a straight line with a slope of −4250 K is obtained. Calculate ‘Ea’ for the reaction.(R = 8.314 JK−1 mol−1)
Solution
`log k=logA-E_a/2.303R(1/T)`
Ea → Activation energy
The above equation is like y = mx + c where if we plot y v/s x we get a straight line with slope ‘m’ and intercept ‘c’.
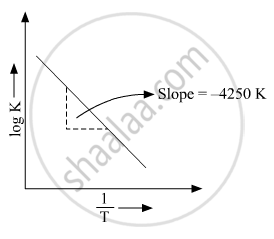
So, slope is equal to`=-E_a/2.303R`
`-E_a/2.303R=-4250k=>E_a=4250 xx 2.303 xx 8.314 =81,375.3535 j mol^(-1)`
`E_a=81.3753 KJ mol^(-1)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Consider the reaction
`3I_((aq))^-) +S_2O_8^(2-)->I_(3(aq))^-) + 2S_2O_4^(2-)`
At particular time t, `(d[SO_4^(2-)])/dt=2.2xx10^(-2)"M/s"`
What are the values of the following at the same time?
a. `-(d[I^-])/dt`
b. `-(d[S_2O_8^(2-)])/dt`
c. `-(d[I_3^-])/dt`
The rate of the chemical reaction doubles for an increase of 10 K in absolute temperature from 298 K. Calculate Ea.
The rate of a reaction quadruples when the temperature changes from 293 K to 313 K. Calculate the energy of activation of the reaction assuming that it does not change with temperature.
Define activation energy.
What is the effect of adding a catalyst on Activation energy (Ea)
Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by ______.
Why does the rate of a reaction increase with rise in temperature?
Why in the redox titration of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] vs oxalic acid, we heat oxalic acid solution before starting the titration?
What happens to most probable kinetic energy and the energy of activation with increase in temperature?
An exothermic reaction X → Y has an activation energy 30 kJ mol-1. If energy change ΔE during the reaction is - 20 kJ, then the activation energy for the reverse reaction in kJ is ______.
