Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
ln which pair highest oxidation states of transition metals are found:
विकल्प
nitriles and chlorides
fluorides and chlorides
fluorides and oxides
nitriles and oxides
उत्तर
fluorides and oxides
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why do interstitial compounds have higher melting points than corresponding pure metals?
Explain why is Fe3+ more stable than Fe2+?
In 3d series (Sc to Zn), which element has the lowest enthalpy of atomisation and why?
Give reasons: Transition metals show variable oxidation states.
What are the transition elements? Write two characteristics of the transition elements.
The `E_((M^(2+)//M))^Θ` value for copper is positive (+0.34 V). What is possibly the reason for this? (Hint: consider its high ΔaHΘ and low ΔhydHΘ)
Predict which of the following will be coloured in the aqueous solution?
Ti3+, V3+, Cu+, Sc3+, Mn2+, Fe3+ and Co2+. Give reasons for each.
Which metal in the first series of transition metals exhibits +1 oxidation state most frequently and why?
What are inner transition elements?
How would you account for the following?
Zr (Z = 40) and Hf (Z = 72) have almost identical radii.
Write balanced chemical equations for the conversion of `CrO_4^(2-)` to `Cr_2O_7^(2-)` in acidic medium and `Cr_2O_7^(2-)` to `CrO_4^(2-)`
in basic medium.
Why does the density of transition elements increase from Titanium to Copper? (at. no. Ti = 22,
Cu = 29)
Why do transition metal ions possess a great tendency to form complexes?
How is potassium dichromate prepared from chrome iron ore?
Read the passage given below and answer the following question:
The transition metals when exposed to oxygen at low and intermediate temperatures form thin, protective oxide films of up to some thousands of Angstroms in thickness. Transition metal oxides lie between the extremes of ionic and covalent binary compounds formed by elements from the left or right side of the periodic table. They range from metallic to semiconducting and deviate by both large and small degrees from stoichiometry. Since electron bonding levels are involved, the cations exist in various valence states and hence give rise to a large number of oxides. The crystal structures are often classified by considering a cubic or hexagonal close-packed lattice of one set of ions with the other set of ions filling the octahedral or tetrahedral interstices. The actual oxide structures, however, generally show departures from such regular arrays due in part to distortions caused by packing of ions of different size and to ligand field effects. These distortions depend not only on the number of d-electrons but also on the valence and the position of the transition metal in a period or group.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion: Crystal structure of oxides of transition metals often show defects.
Reason: Ligand field effect cause distortions in crystal structures.
Read the passage given below and answer the following question:
The transition metals when exposed to oxygen at low and intermediate temperatures form thin, protective oxide films of up to some thousands of Angstroms in thickness. Transition metal oxides lie between the extremes of ionic and covalent binary compounds formed by elements from the left or right side of the periodic table. They range from metallic to semiconducting and deviate by both large and small degrees from stoichiometry. Since electron bonding levels are involved, the cations exist in various valence states and hence give rise to a large number of oxides. The crystal structures are often classified by considering a cubic or hexagonal close-packed lattice of one set of ions with the other set of ions filling the octahedral or tetrahedral interstices. The actual oxide structures, however, generally show departures from such regular arrays due in part to distortions caused by packing of ions of different size and to ligand field effects. These distortions depend not only on the number of d-electrons but also on the valence and the position of the transition metal in a period or group.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion: Transition metals form protective oxide films.
Reason: Oxides of transition metals are always stoichiometric.
Metallic radii of some transition elements are given below. Which of these elements will have highest density?
| Element | \[\ce{Fe}\] | \[\ce{Co}\] | \[\ce{Ni}\] | \[\ce{Cu}\] |
| Metallic radii/pm | 126 | 125 | 125 | 128 |
When \[\ce{KMnO4}\] solution is added to oxalic acid solution, the decolourisation is slow in the beginning but becomes instantaneous after some time because ______.
\[\ce{KMnO4}\] acts as an oxidising agent in acidic medium. The number of moles of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] that will be needed to react with one mole of sulphide ions in acidic solution is ______.
Ionisation enthalpies of Ce, Pr and Nd are higher than Th, Pa and U. Why?
Transition metals can act as catalysts because these can change their oxidation state. How does \[\ce{Fe(III)}\] catalyse the reaction between iodide and persulphate ions?
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the following questions:
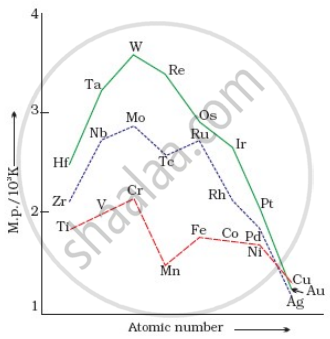
- Why Manganese has lower melting point than Chromium?
- Why do transition metals of 3d series have lower melting points as compared to 4d series?
- In the third transition series, identify and name the metal with the highest melting point.
If enthalpies of formation of C2H4(g), CO2(g) and H2O(l) at 25°C and 1 atm pressure are 52, – 394 and – 286 kJ/mol respectively, the change in ethalpy for combustion of C2H4 is equal to
The spin magnetic moment of cobalt in the compound Hg [Co(SCN)4] is:-
Which of the following maxm magnetic moment?
Account for the following:
Ce4+ is a strong oxidising agent.
Account for the following:
Eu2+ with electronic configuration [Xe]4f76s2 is a strong reducing agent.
Give two similarities in the properties of Sc and Zn.
Explain the use of different transition metals as catalysts.
